In a world increasingly influenced by health vocabulary, wellness fads, and medical advancements, the language we use to discuss our well-being is evolving just as rapidly.
From fitness enthusiasts scrolling through social media for the latest diet tips to healthcare professionals dissecting complex medical terminology, understanding English vocabulary related to health has never been more essential.
But what if mastering this vocabulary could not only enhance your communication skills but also empower you to make informed decisions about your personal health?
English Vocabulary about Health
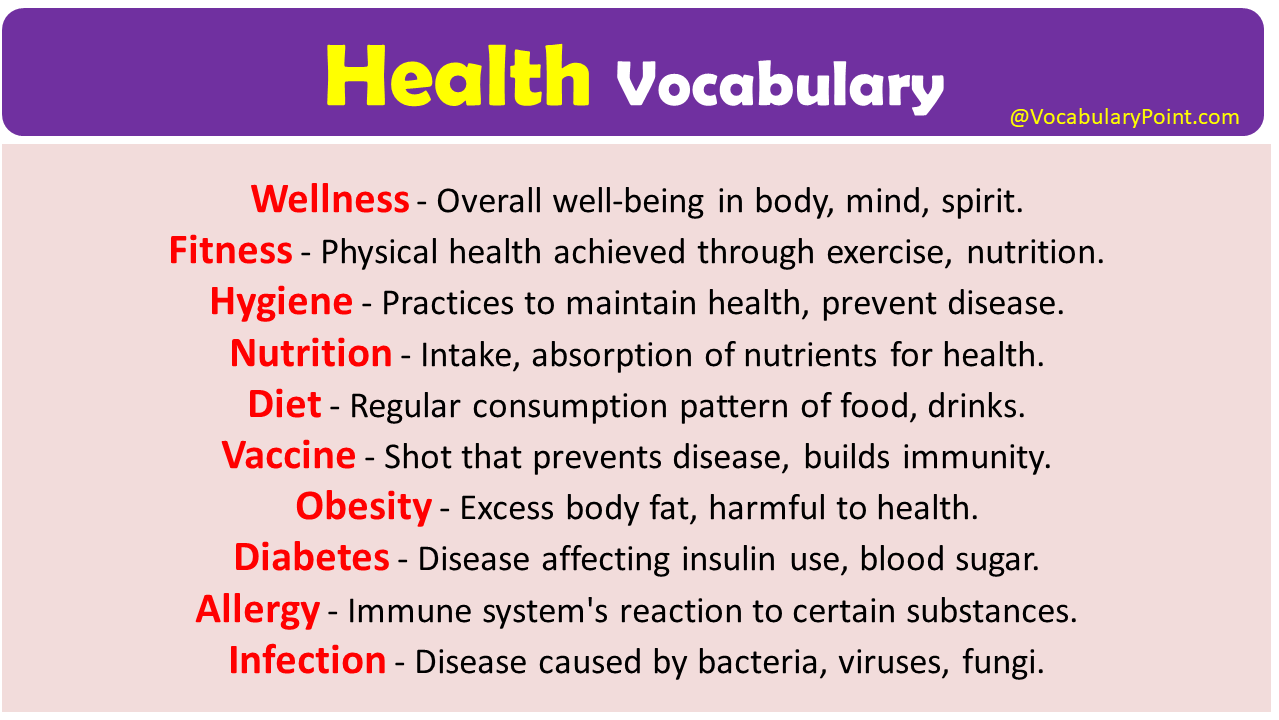
- Wellness – Overall well-being in body, mind, spirit.
- Fitness – Physical health achieved through exercise, nutrition.
- Hygiene – Practices to maintain health, prevent disease.
- Nutrition – Intake, absorption of nutrients for health.
- Diet – Regular consumption pattern of food, drinks.
- Vaccine – Shot that prevents disease, builds immunity.
- Obesity – Excess body fat, harmful to health.
- Diabetes – Disease affecting insulin use, blood sugar.
- Allergy – Immune system’s reaction to certain substances.
- Infection – Disease caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi.
- Chronic – Long-lasting condition, opposite of acute.
- Acute – Severe, sudden onset, short-term condition.
- Fatigue – Extreme tiredness, often from illness, stress.
- Therapy – Treatment for physical, mental health issues.
- Medication – Drugs used to treat or prevent illness.
- Surgery – Medical procedure involving body tissue manipulation.
- Pain – Unpleasant sensory, emotional experience linked injury.
- Stress – Body’s response to demanding or threatening situations.
- Depression – Mood disorder causing persistent sadness, loss.
- Anxiety – Feelings of worry, nervousness, or unease.
- Fracture – Break in bone from trauma, stress.
- Immune System – Body’s defense against infectious organisms, pathogens.
- Symptom – Physical or mental feature indicating condition.
- Virus – Microscopic agent infecting living organisms, cells.
- Bacteria – Single-celled organisms, some causing disease.
- Fungi – Group of spore-producing organisms feeding organically.
- Inflammation – Body’s response to injury, infection.
- Cardiovascular – Pertaining to heart and blood vessels.
- Respiratory – Relating to breathing or the lungs.
- Digestive – Concerning the process of digesting food.
- Neurological – Related to brain, spinal cord, nerves.
- Psychological – Pertaining to mind, emotional state.
- Cancer – Disease with uncontrolled cell growth, spread.
- Hypertension – Medical term for high blood pressure.
- Pediatrics – Branch of medicine dealing with children.
- Geriatrics – Health care for elderly people.
- Radiology – Medical use of imaging to diagnose.
- Orthopedics – Branch of medicine treating bone issues.
- Dermatology – Medical study of skin, its diseases.
- Gastroenterology – Study of stomach, intestinal diseases.
- Obstetrics – Care of women during pregnancy, childbirth.
- Gynecology – Health care for female reproductive systems.
- Ophthalmology – Medical study of eye diseases, conditions.
- Urology – Branch of medicine for urinary system.
- ENT – Ear, Nose, Throat medical specialty.
- Pathology – Study of disease causes, effects.
- Epidemiology – Study of disease patterns in populations.
- Pharmacology – Study of drug effects, uses.
- Rehabilitation – Helping restore health, ability after illness.
- Prevention – Taking steps to avoid disease occurrence.
Explore More:
English Vocabulary words A to Z
Nutrition Vocabulary
- Calories – Units of energy from food intake.
- Carbohydrates – Main energy source, includes sugars, starches.
- Protein – Essential for body repair, muscle growth.
- Fats – Concentrated energy source, essential for health.
- Vitamins – Organic compounds, crucial for body processes.
- Minerals – Inorganic elements that support bodily functions.
- Fiber – Indigestible part of plant-based foods.
- Antioxidants – Compounds that fight cellular damage, aging.
- Micronutrients – Vitamins and minerals needed in small amounts.
- Macronutrients – Nutrients required in large amounts daily.
- Cholesterol – Fat-like substance, essential yet sometimes harmful.
- Saturated Fat – Fat type that can increase cholesterol.
- Unsaturated Fat – Healthier fats, help reduce heart risks.
- Trans Fat – Artificial fats, harmful, increase heart disease.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids – Essential fats, good for heart health.
- Gluten – Protein in wheat, harmful for some.
- Lactose – Sugar in milk, difficult for some.
- Caffeine – Stimulant found in coffee, tea.
- Organic – Foods grown without synthetic pesticides, fertilizers.
- Whole Grains – Grains containing entire kernel; very nutritious.
- Refined Grains – Grains stripped of bran, nutrients.
- Probiotics – Beneficial bacteria, aid digestion, immunity.
- Prebiotics – Compounds that feed beneficial gut bacteria.
- Glycemic Index – Measures food’s impact on blood sugar.
- Electrolytes – Minerals aiding in nerve, muscle function.
- Phytonutrients – Plant compounds with health-promoting properties.
- Water-soluble Vitamins – Vitamins B and C, need replenishment.
- Fat-soluble Vitamins – Vitamins A, D, E, K, stored longer.
- Trace Elements – Minerals needed in very small amounts.
- Enzymes – Proteins that speed up chemical reactions.
- Whole Foods – Foods minimally processed, not refined.
- Processed Foods – Foods altered from their natural state.
- Dietary Fiber – Plant material that aids bowel health.
- Plant-based Diet – Diet consisting primarily of plant foods.
- Animal-based Proteins – Proteins derived from meat, dairy products.
- Balanced Diet – Diet including all nutrient groups sufficiently.
- Meal Planning – Organizing meals to meet nutritional needs.
- Supplements – Products taken to boost nutrient intake.
- Dehydration – Excessive loss of body water.
- Nutrient Density – Amount of nutrients per calorie consumed.
- Empty Calories – Calories from sugar, fats with nutrients.
- Metabolism – Processes by which food is converted.
- Body Mass Index (BMI) – Measure relating weight to height.
- Overnutrition – Excessive nutrient and energy intake.
- Undernutrition – Inadequate intake of nutrients and energy.
- Food Pyramid – Guide outlining what to eat daily.
- Food Plate – Model for healthy eating, portion control.
- Detox – Short-term dietary intervention to remove toxins.
- Superfoods – Foods exceptionally high in nutrients.
- Food Security – Access to sufficient, safe, nutritious food.
Fitness Vocabulary
- Aerobic – Exercises increasing heart rate, breathing rate.
- Anaerobic – Intense, short burst activity without oxygen.
- Cardiovascular – Pertaining to heart and blood vessels.
- Strength Training – Exercises designed to increase muscle strength.
- Flexibility – Ability to move joints through full range.
- Endurance – Ability to sustain prolonged physical activity.
- Resistance Training – Exercises using resistance to strengthen muscles.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) – Alternating short bursts of intense exercise, rest.
- Circuit Training – Series of exercises performed in rotation.
- Body Composition – Ratio of fat to lean tissue.
- Cool Down – Low-intensity exercise to return to normal.
- Warm-Up – Light activities prepping muscles for workout.
- Reps – Short for repetitions, one exercise cycle.
- Sets – Group of consecutive repetitions.
- Core Training – Exercises that target torso muscles.
- Plyometrics – Jump training to increase power.
- Cross-Training – Combining different exercises for balanced fitness.
- Personal Trainer – Certified individual coaching others in fitness.
- Calisthenics – Gymnastics exercises to achieve bodily fitness.
- Bodybuilding – Sport involving muscle development through lifting.
- Toning – Light weight training for muscle definition.
- Spinning – Stationary cycling workout, high intensity.
- Yoga – Practice combining posture, breathing, and meditation.
- Pilates – Exercise focusing on core strength, flexibility.
- Kickboxing – Combines boxing with cardiovascular exercise.
- Interval Training – Alternating short, high-intensity and recovery periods.
- Stretching – Exercises aiming to increase flexibility.
- Functional Training – Exercises focusing on practical movement patterns.
- Kettlebell – Weight used for ballistic exercise routines.
- Zumba – Dance fitness program for body conditioning.
- Boot Camp – High-intensity, military-style physical training.
- Balance Exercises – Activities improving physical stability, prevent falls.
- Aqua Aerobics – Water-based aerobic exercise, gentle on joints.
- Bodyweight Exercises – Using own weight for resistance training.
- Physical Therapy – Rehab exercises to restore, enhance function.
- Lactic Acid – Substance produced during intense exercise.
- Metabolism – Processes converting food into energy.
- Nutrition – Dietary habits impacting fitness performance.
- Recovery – Rest periods allowing muscle repair.
- Overtraining – Excessive workout leading to diminished returns.
- Tabata – Form of high-intensity interval training.
- Barre – Workout combining ballet, Pilates, yoga.
- Marathon – Long-distance running race, 26.2 miles.
- Triathlon – Competitive event swimming, cycling, running.
- Dumbbells – Weights for resistance training.
- Gymnasium – Facility equipped for physical exercise.
- Heart Rate – Number of heart beats per minute.
- Sports Nutrition – Dietary practice enhancing athletic performance.
- Cooldown – Low-intensity exercise to reduce heart rate.
- Spotting – Assisting another during weightlifting exercises.