Military vocabulary encompasses the specialized terminology and jargon used within the armed forces to describe strategies, operations, ranks, equipment, and procedures. This language is essential for clear communication in high-pressure situations, ensuring that soldiers, officers, and military personnel understand commands and coordinate efficiently.
Whether discussing logistics, combat tactics, or technological advancements, military vocabulary plays a vital role in unifying personnel across different branches and units. For those inside or outside the military, having a grasp of these terms can provide valuable insight into the structure, function, and culture of armed forces around the world.
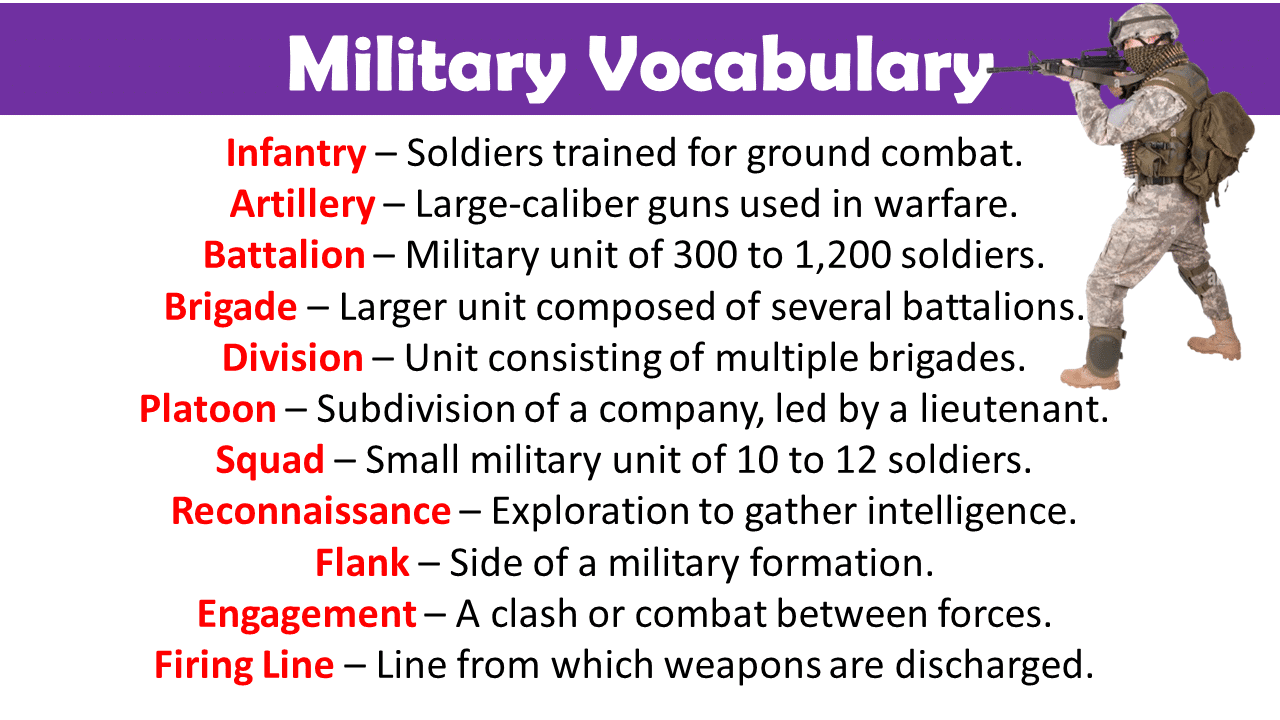
Military Vocabulary Words
- Infantry – Soldiers trained for ground combat.
- Artillery – Large-caliber guns used in warfare.
- Battalion – Military unit of 300 to 1,200 soldiers.
- Brigade – Larger unit composed of several battalions.
- Division – Unit consisting of multiple brigades.
- Platoon – Subdivision of a company, led by a lieutenant.
- Squad – Small military unit of 10 to 12 soldiers.
- Reconnaissance – Exploration to gather intelligence.
- Flank – Side of a military formation.
- Engagement – A clash or combat between forces.
- Firing Line – Line from which weapons are discharged.
- Enlistment – Volunteering for military service.
- Commission – Formal appointment as an officer.
- Command – Authority over military forces.
- Combatant – Soldier actively engaged in combat.
- Cavalry – Soldiers on horseback, now mechanized units.
- Warhead – Explosive device carried by a missile.
- Sniper – Marksman skilled in shooting from concealed positions.
- Defensive Position – Fortified location for defense.
- Fireteam – Small unit of four soldiers.
- LZ (Landing Zone) – Area designated for aircraft landing.
- AWOL (Absent Without Leave) – Unauthorized absence from duty.
- Armistice – Formal agreement to cease hostilities.
- Bunker – Reinforced shelter, often underground.
- Chain of Command – Hierarchical system of authority.
- Fire Support – Use of artillery or aircraft to support ground troops.
- Logistics – Coordination of supplies and equipment.
- Insurgency – Uprising against a government or authority.
- MRE (Meal, Ready-to-Eat) – Pre-packaged field ration.
- Demolition – Destruction of structures, often using explosives.
- Dog Tags – Metal identification worn by soldiers.
- Drill – Practice exercise to improve military skills.
- Enfilade – Gunfire directed along the length of a target.
- Espionage – Intelligence gathering by covert means.
- Evacuation – Removal of troops or civilians from a danger zone.
- Garrison – Troops stationed in a particular location.
- Infiltration – Covert entry into enemy territory.
- Interrogation – Questioning of captured enemies.
- KIA (Killed in Action) – Soldier killed during combat.
- Mortar – Short-barreled artillery for indirect fire.
- Paratrooper – Soldier trained to parachute into combat.
- Quartermaster – Officer in charge of supplies.
- Ration – Portion of food allotted to soldiers.
- Recon – Short for reconnaissance; scouting for intelligence.
- Regiment – Unit consisting of several battalions.
- Reserves – Military forces not on active duty but available.
- Rifleman – Soldier armed with a rifle.
- Sabotage – Deliberate destruction of equipment or infrastructure.
- Salvo – Simultaneous discharge of artillery or firearms.
- Sortie – A single military flight or mission.
- Tactical – Related to battlefield maneuvers and combat strategy.
- Tank – Armored vehicle with heavy firepower.
- Torso Plate – Body armor designed to protect the chest.
- Tracer – Ammunition with a visible light trail for targeting.
- Volley – Multiple projectiles launched simultaneously.
- IED (Improvised Explosive Device) – Homemade bomb.
- IED Jammer – Device used to disrupt IED signals.
- Base of Fire – Position providing covering fire for advancing troops.
- Breach – Breaking through an enemy’s defenses.
- Bridgehead – Secure area established by invading forces.
- Casualty – A soldier who is injured, killed, or missing.
- Conscript – Individual drafted into military service.
- Convoy – Group of vehicles traveling together for protection.
- Counteroffensive – Attack launched in response to an enemy’s advance.
- Coup – Overthrow of a government by force.
- Decoy – Object or tactic used to distract the enemy.
- Depth Charge – Explosive dropped into the water to combat submarines.
- Deploy – Movement of troops into position for action.
- Detachment – A small unit sent on a special mission.
- Doctrine – Set of principles guiding military operations.
- Draft – Mandatory enlistment for military service.
- Dugout – Shelter dug into the ground for protection.
- Escort – Armed protection for personnel or vehicles.
- Flare – Device emitting light to signal or illuminate.
- Flechette – Small metal dart used as ammunition.
- Flight Deck – Area on an aircraft carrier where aircraft take off and land.
- Foot Patrol – Ground-based surveillance or reconnaissance.
- Fumigation – Use of chemicals to clear out enemy forces.
- Guerrilla – Small, mobile forces using irregular tactics.
- Hatch – Opening in a ship or tank.
- Honor Guard – Soldiers responsible for ceremonial duties.
- Hostile Fire – Gunfire from enemy forces.
- IED Detector – Device used to locate hidden explosives.
- Imminent Threat – Immediate danger requiring quick action.
- Improvise – Create a makeshift solution under pressure.
- Insertion – Placement of forces into a combat area.
- Joint Operation – Mission involving multiple branches of the military.
- Lance Corporal – Junior rank in some military forces.
- Landmine – Explosive device buried in the ground.
- Lethal Force – Use of force likely to cause death.
- Lieutenant – Junior officer rank in the military.
- Maneuver Warfare – Tactics aimed at outflanking the enemy.
- Medal of Honor – Highest U.S. military award for valor.
- Medivac (Medical Evacuation) – Removal of injured personnel from the battlefield.
- Missile Defense – Systems designed to intercept and destroy missiles.
- Napalm – Flammable liquid used in warfare.
- No Man’s Land – Unoccupied territory between enemy lines.
- Observation Post – Location used for surveillance.
- Ordnance – Military weapons, ammunition, and explosives.
- Outflank – Maneuver to move around the enemy’s side.
- Overwatch – Providing covering fire or observation for another unit.
- Patrol – Unit sent out to gather intelligence or protect an area.
- Peacekeeping – Military operations aimed at maintaining peace.
- Phalanx – Military formation of soldiers with shields and spears.
- Pincer Movement – Military maneuver to surround an enemy.
- Private First Class – Enlisted rank above private.
- Quarters – Living accommodations for soldiers.
- Rank – Position or level of authority in the military hierarchy.
- Rappel – Descend from a height using a rope.
- Retreat – Withdrawal of forces from combat.
- Riot Control – Operations to manage and disperse crowds.
- Saturation Bombing – Intense bombing over a large area.
- Scorched Earth – Destruction of resources to deny them to the enemy.
- Search and Rescue – Mission to locate and recover personnel.
- Secure – To gain control of an area or objective.
- Seige – Prolonged military blockade of a fortified place.
- Shelter-in-place – Taking refuge in a safe location.
- Shrapnel – Fragments from an exploding bomb or shell.
- Skirmish – Small, brief combat encounter.
- Snatch and Grab – Quick operation to capture a target.
- Sortie – One mission or flight by a single aircraft.
- Standoff – Situation where opposing forces are unable to advance.
- Stealth – Military tactic for avoiding detection.
- Submarine – Underwater military vessel.
- Suppressive Fire – Gunfire used to prevent the enemy from returning fire.
- Tactical Retreat – Planned withdrawal for strategic advantage.
- Theater of War – Region where active military operations occur.
- Tracer Round – Ammunition that emits light when fired.
- Troop Carrier – Vehicle used to transport soldiers.
- Triage – System for prioritizing medical care on the battlefield.
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) – Drone used for surveillance or attack.
- Veteran – Former member of the armed forces.
- Victory – Success in achieving military objectives.
- War Crimes – Violations of international law during armed conflict.
- War Games – Simulated military exercises.
- Watchtower – Elevated structure for observation.
- Weapons Cache – Hidden storage of weapons.
- Weapons-Free Zone – Area where use of weapons is restricted.
- Withdrawal – Planned departure from a combat zone.
- Wingman – Aircraft flying next to the lead plane.
- Zero Hour – Time set for the start of a military operation.
- Zonal Defense – Defense strategy based on territorial control.
- Armor-Piercing – Ammunition designed to penetrate armor.
- Assault – Attack on an enemy position.
- Ballistic Missile – Projectile that follows a parabolic flight path.
- Battlefront – Area where active combat is taking place.
- Bayonet – Blade attached to the end of a rifle.
- Bivouac – Temporary encampment without tents.
- Blockade – Preventing access to an area by enemy forces.
- Booby Trap – Hidden explosive device.
- Camouflage – Disguise to blend into surroundings.
- Carbine – Shorter version of a rifle.
- Checkpoint – Controlled access point for security purposes.
- Civilians – Non-military personnel in a warzone.
- Close Quarters Combat (CQC) – Combat at close range.
- Covert Operations – Secretive military activities.
- Depth Charge – Explosive used to combat submarines.
- Directive – Command issued by a superior officer.
- Dogfight – Aerial combat between fighter planes.
- Drop Zone – Area where paratroopers land.
- Field Hospital – Temporary medical facility in a combat zone.
- Frag Grenade – Hand-thrown explosive.
- Friendly Fire – Accidental attack on one’s own forces.
- Grenade Launcher – Device for firing grenades.
- Hand-to-Hand Combat – Close combat without firearms.
- Hot Zone – Area of intense military activity.
- Intel – Information gathered for military purposes.
- Interdiction – Preventing enemy movement or supplies.
- Landing Craft – Boat used to transport troops to shore.
- Logbook – Record of missions or operations.
- Machine Gun Nest – Fortified position for a machine gun.
- Maneuver – Strategic movement of military forces.
- Mercenary – Soldier for hire.
- Militia – Civilian military force.
- Minefield – Area containing hidden explosives.
- Munition – Military weapons and ammunition.
- Mutiny – Rebellion against authority within the military.
- Napalm Strike – Attack using flammable gel.
- Naval Blockade – Use of ships to prevent maritime access.
- Nuclear Deterrent – Strategy using the threat of nuclear retaliation.
- Observation Tower – High structure for surveillance.
- Parade Ground – Area for military drills and ceremonies.
- Perimeter Defense – Protection of the outer boundary of a base.
- Pistol – Handheld firearm.
- Platoon Leader – Officer in charge of a platoon.
- Quarantine – Isolation of troops or areas to prevent the spread of disease.
- Raider – Soldier or group conducting surprise attacks.
- Rearguard – Forces protecting the rear of a formation.
- Recon Platoon – Unit specializing in scouting missions.
- ROE (Rules of Engagement) – Guidelines for military combat.
- Rover Patrol – Mobile unit monitoring an area.
- SAM (Surface-to-Air Missile) – Missile designed to shoot down aircraft.
- Sandbag – Bag filled with sand for fortifications.
- Seismic Sensor – Device detecting ground movement.
- Shock Troops – Soldiers trained for aggressive combat.
- Siege Tower – Large structure for scaling enemy walls.
- Signal Corps – Unit responsible for military communications.
- Skirmisher – Soldier engaging in light combat.
- Smoke Grenade – Device creating a smoke screen.
- Task Force – Temporary military group formed for a specific mission.
Explore More Words:

Military Vocabulary List
- Amphibious Assault – Attack launched from the sea onto land.
- Anti-Aircraft – Weapons designed to destroy aircraft.
- Armory – Facility where weapons and ammunition are stored.
- Artillery Battery – Group of artillery pieces operating together.
- Asymmetric Warfare – Conflict between forces with unequal military strength.
- Auxiliary Forces – Support troops assisting the main combat forces.
- Backblast – Expelled gases from the rear of a rocket or missile.
- Ballistics – Study of the motion of projectiles.
- Barbed Wire – Wire with sharp edges used for defensive purposes.
- Base Camp – Main camp where military operations are directed.
- Battle Dress Uniform (BDU) – Camouflage uniform worn by military personnel.
- Bay of Fire – Area covered by gunfire from a specific point.
- Blast Radius – Area affected by an explosion.
- Blitzkrieg – Rapid and intense military attack.
- Blue Force – Refers to friendly or allied military units.
- Boot Camp – Basic training program for new recruits.
- Breach Point – Location where a defensive line is penetrated.
- Call Sign – Coded identifier used in radio communications.
- Cannon – Large gun typically used in field artillery.
- Casemate – Fortified gun emplacement or armored structure.
- Ceasefire – Temporary suspension of hostilities.
- Chaff – Radar countermeasure using metallic strips to confuse enemy radar.
- Checkpoint Charlie – Famous Cold War crossing point between East and West Berlin.
- Civil Defense – Protection of civilians from military attacks.
- Cold War – Period of geopolitical tension between the U.S. and Soviet Union.
- Combat Air Patrol (CAP) – Aircraft patrolling to protect a specific area.
- Combined Arms – Use of multiple military branches working together in combat.
- Commando – Special forces soldier trained in unconventional warfare.
- Concentration Camp – Prison camp used for detaining enemies or civilians.
- Counterinsurgency – Military operations aimed at defeating an insurgency.
- Cruiser – Fast naval ship designed for long-range offensive operations.
- Defection – Abandonment of one’s country or cause to join the enemy.
- Demobilization – Disbanding of troops after military service.
- Destroyer – Naval ship used for escorting larger vessels and defending against air and submarine attacks.
- Echelon – Formation of troops or units in staggered lines.
- Engagement Zone – Area where combat with the enemy takes place.
- Entrenching Tool – Small foldable shovel used for digging defensive positions.
- Exfiltration – Removal of troops or personnel from a hostile area.
- Field Manual (FM) – Instruction book detailing military tactics and procedures.
- Fire Mission – Command to deliver artillery fire on a target.
- Foxhole – Shallow pit dug by soldiers for cover.
- Freedom Fighter – Individual or group engaging in armed resistance for political freedom.
- Frontal Assault – Direct attack on enemy positions from the front.
- Ghillie Suit – Camouflage clothing used by snipers.
- Glider – Aircraft without an engine, used for silent infiltration of troops.
- Green Beret – Member of U.S. Army Special Forces.
- Gunboat Diplomacy – Use of naval force to achieve diplomatic objectives.
- Half-Track – Armored vehicle with wheels in the front and tracks in the rear.
- Harassment Fire – Light, sporadic gunfire used to disrupt enemy movements.
- Heliport – Designated area for helicopter takeoffs and landings.
- High-Explosive Round – Shell designed to cause maximum destruction through explosive force.
- Howitzer – Long-range artillery piece with a high trajectory.
- IED (Improvised Explosive Device) – A bomb constructed and deployed in unconventional ways.
- Insurgent – Member of a rebel group opposing a government.
- Kill Box – Predefined area where military forces are authorized to engage enemy targets.
- Kinetic Strike – Attack using physical force rather than explosives or chemicals.
- Knee Mortar – Portable, lightweight mortar used in infantry combat.
- Lance Missile – Tactical surface-to-surface missile.
- Laser-Guided Bomb – Bomb guided to its target using laser technology.
- Logistics Train – System of transporting supplies and reinforcements to the battlefield.
- Low Crawl – Technique where soldiers move close to the ground to avoid detection.
- Maneuverability – Ability of military units or vehicles to change position or direction quickly.
- Marines – Naval infantry force trained for amphibious operations.
- Martial Law – Temporary rule by military authorities during emergencies.
- Minefield – Area containing explosive mines.
- Monsoon Season – Seasonal period of heavy rainfall affecting military operations.
- Mountain Warfare – Military operations conducted in mountainous terrain.
- Night Vision Goggles (NVG) – Devices that allow soldiers to see in low-light conditions.
- No-Fly Zone – Area where aircraft are not permitted to fly, enforced by military means.
- Observer – Person assigned to watch enemy movements and report intelligence.
- Offensive – Large-scale military attack aimed at defeating the enemy.
- Operations Order (OPORD) – Detailed plan outlining military actions.
- Overlord (Operation) – Code name for the Allied invasion of Normandy in World War II.
- Overwatch – Position from which troops provide covering fire for other units.
- Pacific Theater – Region of military operations in the Pacific during World War II.
- Partisan – Member of a resistance movement or guerrilla force.
- Penetration – Breakthrough into enemy defenses.
- Pincer Attack – Military maneuver in which the enemy is attacked from two sides.
- Platoon Leader – Officer in command of a platoon.
- Plinking – Slang term for precision targeting, typically against vehicles.
- Point Man – Soldier leading a patrol or combat unit.
- Post Exchange (PX) – Military retail store selling goods to service members.
- QRF (Quick Reaction Force) – Unit prepared to respond immediately to threats.
- Quarters – Living accommodations provided to military personnel.
- R&R (Rest and Recuperation) – Leave for soldiers to recover from combat fatigue.
- Rail Gun – Weapon that uses electromagnetic force to launch projectiles.
- Range Finder – Device used to determine the distance to a target.
- Rear Admiral – Senior naval officer rank.
- Reconnaissance by Fire – Firing into an area to provoke the enemy into revealing their position.
- Retaliatory Strike – Military attack in response to an enemy assault.
- Reveille – Bugle call signaling the start of the day in military camps.
- Rolling Thunder (Operation) – U.S. bombing campaign during the Vietnam War.
- Rules of Engagement (ROE) – Guidelines dictating when and how military force can be used.
- Sabre Rattling – Aggressive demonstration of military power.
- Sapper – Soldier trained in engineering duties such as demolitions and fortifications.
- Scuttling – Deliberate sinking of a ship to prevent its capture.
- Searchlight – Powerful light used to illuminate enemy positions or aircraft.
- Shore Battery – Coastal gun emplacements defending against naval attacks.
- Silent Drill – Precision military drill performed without verbal commands.
- Sky Marshal – Armed law enforcement officer on commercial aircraft.
- Snatch and Grab – Quick raid to capture a specific target.
- Sortie – A single flight or mission by an aircraft.
- Spearhead – Leading element in a military attack.
- Standing Orders – Permanent instructions issued to military units.
- Standoff Weapon – Weapon fired from a distance, allowing the operator to remain out of range.
- Strategic Bomber – Aircraft designed for long-range bombing missions.
- Strike Force – Group of forces organized for a specific combat mission.
- Sunken Road – Depression in a battlefield providing cover for troops.
- Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) – Missile designed to target aircraft.
- Sword Arm – Military term for offensive capabilities.