FINITE AND NON FINITE VERBS EXAMPLES. Here is a list of finite or non-finite verbs with examples and pdf with detailed lesson. DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FINITE OR NON FINITE VERBS, A finite verb is a verb that has a tense (past, present, future) and can serve as the main verb in a sentence, expressing a complete thought. It also agrees with the subject in person and number. For example, “She sings,” “They run,” “I am studying.”
A non-finite verb is a verb that does not have tense and cannot serve as the main verb in a sentence. It does not agree with the subject in person and number. Examples include infinitives (to run), participles (running), and gerunds (running). Non-finite verbs often function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs in a sentence.
Must learn: infinitive gerund and participles
FINITE AND NON FINITE VERBS EXAMPLES

10 sentences differences between finite or non-finite verb?
- Finite verbs indicate tense and have a subject-verb agreement, while non-finite verbs do not show tense and do not require subject-verb agreement.
- Finite verbs can act as the main verb in a sentence, while non-finite verbs cannot.
- Finite verbs are usually marked by inflection for tense, mood, voice, and agreement, while non-finite verbs do not have such inflections.
- The subject of a sentence determines the form of the finite verb, while non-finite verbs do not depend on the subject.
- Finite verbs typically appear as the first verb in a sentence, while non-finite verbs typically appear after the subject.
- Finite verbs can stand alone as a complete clause, while non-finite verbs need to be accompanied by a finite verb to form a complete clause.
- Finite verbs have a specific tense, such as past, present, or future, while non-finite verbs do not have a tense.
- Finite verbs can express action or state, while non-finite verbs can only express action.
- Finite verbs are used to convey the main message of a sentence, while non-finite verbs provide additional information to the sentence.
- Finite verbs can be modified by adverbs, while non-finite verbs cannot be modified by adverbs.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FINITE OR NON FINITE VERBS
In many languages, a single verb may have several different forms which form different grammatical functions. These forms are often divided into two types:
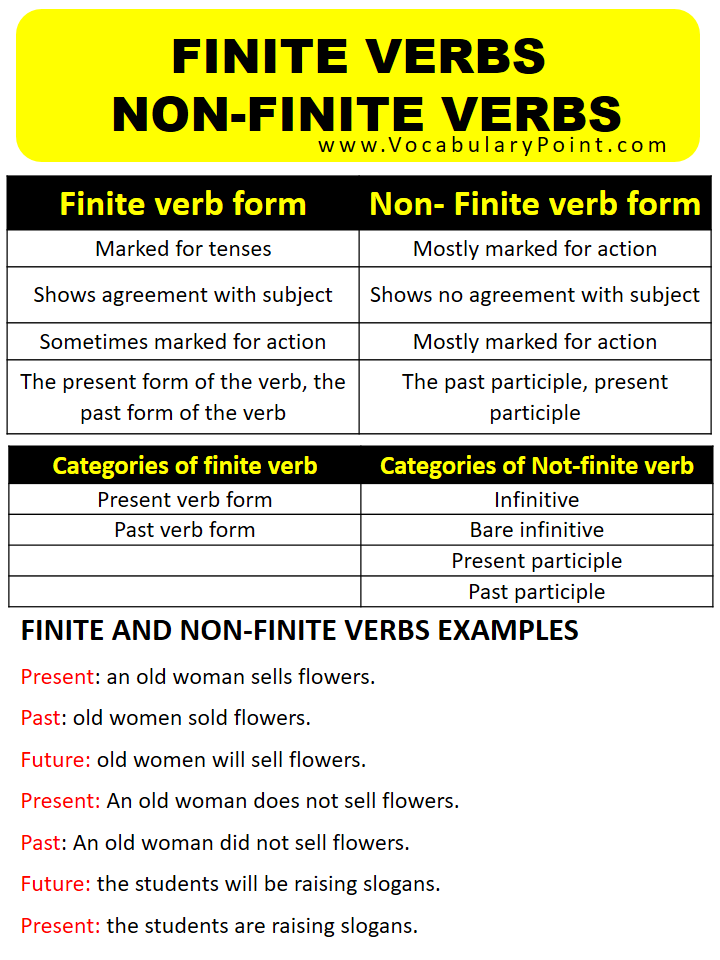
| Finite verb form | Non- Finite verb form |
| · Marked for tenses | · Mostly marked for action |
| · Shows agreement with subject | · Shows no agreement with subject |
| · Sometimes marked for action | · Mostly marked for action |
| · The present form of the verb, the past form of the verb | · The past participle, present participle |
Categories of finite and non-finite
| Categories of finite verb | Categories of Not-finite verb |
| Present verb form | Infinitive |
| Past verb form | Bare infinitive |
| Present participle | |
| Past participle |
FINITE AND NON-FINITE VERBS EXAMPLES
Present: an old woman sells flowers.
Past: old women sold flowers.
Future: old women will sell flowers.
Bare infinitive
- The present form of the verb without ‘’to’’.
- Occurs away from the subject.
- Has no agreement with subject
Negative
Present: An old woman does not sell flowers.
Past: An old woman did not sell flowers.
Future: the students will be raising slogans.
Details: in these sentences did, and will are finite verbs, and sell is a bare infinitive verb.
Continuous tense
Present: the students are raising slogans.
Past: the students were raising slogans.
Future: the students will be raising slogans.
Details: in these sentences are were, and will finite verbs and raising
Perfect tense
Present: teacher has marked students’ answer book.
Past: the teacher had marked students’ answer book.
Future: teacher will have marked students’ answers book.
Note: in all interrogative sentences, helping verbs are considered finite verbs, and also other categorizations remain the same.
When a verb is governed by a person and number it is called a finite verb.
Examples
- He went (finite) to his home.
- He went (finite) to his home to rest. (infinitive)

The following are the Nonfinite Verbs:
- Participles
- Gerunds
- Infinitives
PARTICIPLES
- A participle is a form of a verb that is partly a verb and partly an adjective.
- A participle is a double part of speech a verb and adjectives combined.
- A participle does the work of a verb as well as an adjective.
GERUND
A gerund is that form of verb which ends in “ing” and is partly a noun. It is a verbial noun.
- Both gerund and infinitive have the force of a noun and a verb. Therefore, there use are also similar.
- Smoking is injurious to health.
- Smoking word is made by smoke +ing and it is work as a noun and also it is a verb or works as the subject. That’s why it is verb noun and called gerund.
INFINITIVE
The word infinitive is a kind of noun but it also has the feature of the verb.
So we call it verbal noun. The word “to” is used with the infinitive. However, “to” is not used with certain words h as: bid, bear, see, need, dare, hear, make, let.
Example:
- Made him stand.
- We need not go there.
- We bade them leave early.
- He let me know.
- Dare not disobey my parents.
- I saw him come.
- We did not hear him speak.
- You need not work.
You can download FINITE AND NON-FINITE VERBS PDF
