Embarking on the journey of learning human anatomy is an enlightening experience, especially for beginners and students. A unique way to navigate this complex subject is by exploring body parts based on their starting alphabet. In this segment, we focus on body parts that start with ‘W’. Although they might not be as numerous as those starting with other letters, each plays a significant role in the human body.
From the bones in our wrists to the intricate workings of our windpipe, these ‘W’ body parts are integral to various functions, be it movement, protection, breathing, or other vital processes. This curated list aims to provide an engaging and comprehensive insight into these parts for those new to the world of anatomy.
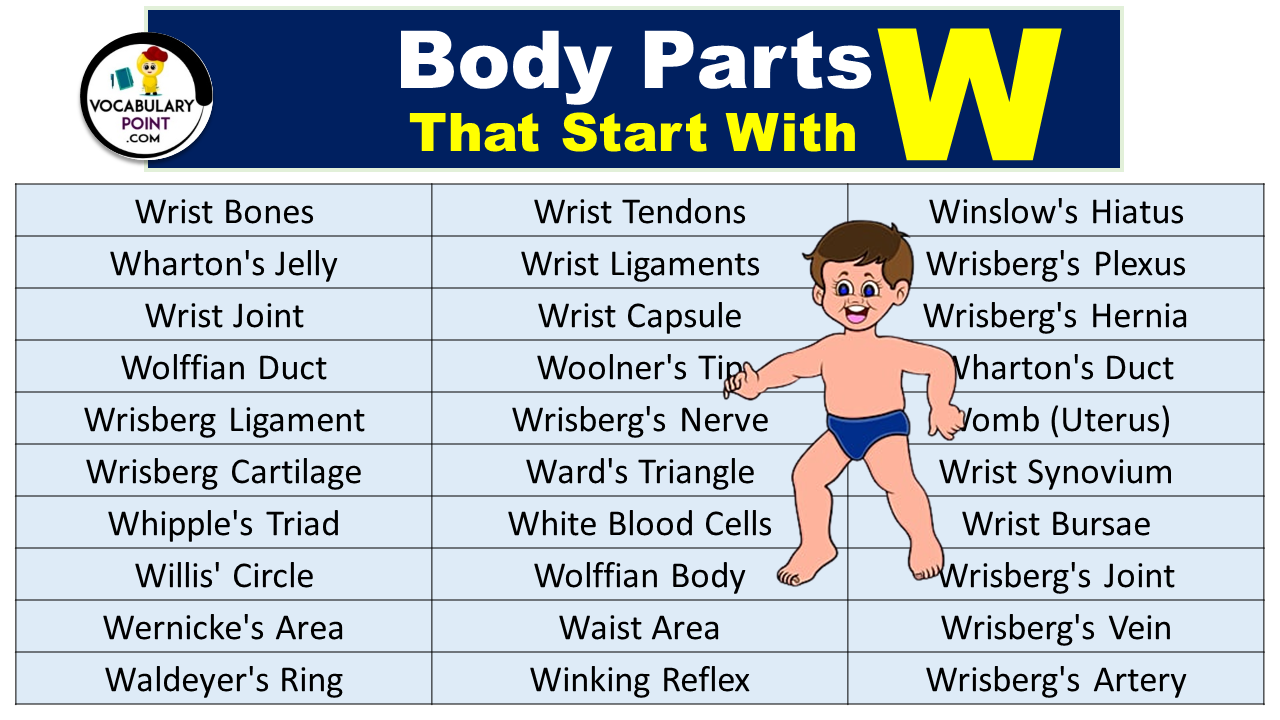
Body Parts That Start With W
- Wrist Bones
- Wharton’s Jelly
- Wrist Joint
- Weberian Apparatus
- Wolffian Duct
- Wrisberg Ligament
- Wrisberg Cartilage
- Whipple’s Triad
- Waterston’s Groove
- Willis’ Circle
- Windpipe (Trachea)
- Wernicke’s Area
- Wrist Flexor Muscles
- Wrist Extensor Muscles
- Waldeyer’s Ring
- Wartenberg’s Syndrome
- Weitbrecht’s Foramen
- Wrist Tendons
- Wrist Ligaments
- Wrist Capsule
- Woolner’s Tip
- Wrisberg’s Nerve
- Ward’s Triangle
- Wartenberg’s Test
- White Matter of Brain
- White Matter of Spinal Cord
- White Blood Cells
- Wolffian Body
- Waist Area
- Winking Reflex
- Wrisberg’s Ganglion
- Wartberg’s Nodule
- Wrisberg’s Medial Meniscus
- Wrisberg’s Lateral Meniscus
- Wolfram Syndrome
- Winslow’s Hiatus
- Winslow’s Foramen
- Wrisberg’s Plexus
- Wrisberg’s Hernia
- Wernicke’s Encephalopathy
- Wharton’s Duct
- Womb (Uterus)
- Weaver’s Bottom
- Wrisberg’s Tendon
- Wrisberg’s Fibers
- Webster’s Procedure
- Wolf’s Law
- Wartenberg’s Sign
- Wrist Synovium
- Wrist Bursae
- Wrist Carpal Tunnel
- Wrist Carpal Bones
- White Fibrocartilage
- White Pulmonary Artery
- White Pulmonary Vein
- White Coats’ Effect
- Wrisberg’s Joint
- Walker-Warburg Syndrome
- Wrisberg’s Vein
- Wrisberg’s Artery
Explore More:
(A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y, Z)

Body Parts Beginning With W (And Their Properties)
- Wrist Bones (Carpals): A set of eight small bones forming the wrist joint.
- Wharton’s Jelly: A gelatinous substance within the umbilical cord, providing cushioning and support.
- Wrist Joint: A complex joint allowing a wide range of hand movements.
- Weberian Apparatus: A specialized structure in fish, aiding in sound transmission.
- Wolffian Duct: A structure in embryonic development, precursor to male reproductive organs.
- Wrisberg Ligament: A ligament in the knee, contributing to joint stability.
- Wrisberg Cartilage: A part of the knee joint, aiding in smooth knee movements.
- Whipple’s Triad: Clinical criteria used for diagnosing insulinoma.
- Waterston’s Groove: An anatomical feature in the lungs, marking the division between lobes.
- Willis’ Circle (Circle of Willis): A ring of arteries at the base of the brain, critical for blood supply.
- Windpipe (Trachea): A tube carrying air to the lungs, crucial for respiration.
- Wernicke’s Area: A brain region involved in language comprehension.
- Wrist Flexor Muscles: Muscles that bend the wrist and fingers.
- Wrist Extensor Muscles: Muscles responsible for extending the wrist and fingers.
- Waldeyer’s Ring: A ring of lymphoid tissue in the throat, part of the immune system.
- Wartenberg’s Syndrome: A neurological disorder affecting the radial nerve.
- Weitbrecht’s Foramen: An anatomical feature related to joint capsules.
- Wrist Tendons: Fibrous tissues connecting muscles to bones in the wrist.
- Wrist Ligaments: Bands of fibrous tissue providing stability to the wrist joint.
- Wrist Capsule: The fibrous tissue surrounding the wrist joint.
- Woolner’s Tip: An anatomical point related to the thyroid gland.
- Wrisberg’s Nerve: A nerve associated with the knee.
- Ward’s Triangle: An area in the femur important in bone density measurements.
- Wartenberg’s Test: A clinical test for nerve injury or disease.
- White Matter of Brain: Nervous tissue involved in the transmission of neural signals.
- White Matter of Spinal Cord: Composed of myelinated nerve fibers, important for nerve signal transmission.
- White Blood Cells (Leukocytes): Cells of the immune system defending the body against infections.
- Wolffian Body: An embryological structure related to the development of the reproductive system.
- Waist Area: The part of the torso between the ribs and the hips.
- Winking Reflex: A reflex action of closing one eye quickly.
Other Body Parts Names Starting With The Letter W
- Weaver’s Bottom
- Wrisberg’s Tendon
- Wrisberg’s Fibers
- Webster’s Procedure
- Wolf’s Law
- Wartenberg’s Sign
- Wrist Synovium
- Wrist Bursae
- Wrist Carpal Tunnel
- Wrist Carpal Bones
- White Fibrocartilage
- White Pulmonary Artery
- White Pulmonary Vein
- White Coats’ Effect
- Wrisberg’s Joint
- Walker-Warburg Syndrome
- Wrisberg’s Vein
- Wrisberg’s Artery
- Wrisberg’s Medial Meniscus
- Wrisberg’s Lateral Meniscus
- Wolfram Syndrome
- Winslow’s Hiatus
- Winslow’s Foramen
- Wrisberg’s Plexus
- Wrisberg’s Hernia
- Wernicke’s Encephalopathy
- Wharton’s Duct
- Womb (Uterus)
- Wrisberg’s Vein
- Wrisberg’s Artery