Direct Indirect speech with examples and rules PDF. When we want to repeat or report what someone has said, we can either use direct speech, where we quote the actual words that were spoken, or indirect speech, where we paraphrase what was said.
Using direct speech in writing can help to create a more vivid picture for the reader, but it is not always necessary or appropriate. For example, if we are reporting on a conversation that took place some time ago, it is usually better to use indirect speech.
- Direct speech is when you quote someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report on what someone said without quoting them directly.
- When we are writing, we often want to share what someone has said. This can be done in two ways: direct and indirect speech. Direct speech is when we quote the person verbatim, while indirect speech is when we paraphrase what they have said. Both have their own set of rules which must be followed.
- Direct speech is easy to use; simply put the words spoken inside quotation marks and write them as they were said. For example, if I wanted to share what my friend said about the party last night, I would write: “She was like, ‘That party was wild!'” It’s important to note that you should only use direct speech if you are 100% sure of what was said; otherwise, it’s best to use indirect speech.
- Indirect speech is a bit more complicated as there are more rules to follow.
- In communication, there is a distinction between direct and indirect speech. Direct speech is where you quote someone verbatim, while indirect speech reports on what somebody said without quoting them directly. Each has its own set of rules.
Here are 10 examples of direct and indirect speech:
- Direct Speech: “I’m going to the store,” she said.
Indirect Speech: She said that she was going to the store.
- Direct Speech: “The store is closed,” he told me.
Indirect Speech: He told me that the store was closed.
- Direct Speech: “I will be there in five minutes,” she promised.
Indirect Speech: She promised that she would be there in five minutes.
- Direct Speech: “Do your homework,” he advised me.
Direct Indirect speech with examples
Direct Speech
What is direct speech? We may quote the actual words used by the speaker is called Direct speech. In this speech we seen, The words quote have been put within quotation marks or inverted commas, There is always a comma, a colon after ‘said’ that introduces the spoken words, in direct speech the exact words of the speaker has been used. Let say Karma said, “I am going market.”
What are the examples of direct speech?
He said, “Hurrah! We have won.”
The boy said to girl, “I can hear you.”
Leo said to his brother, “Why are you crying?
The man said to the children, “I know you and your Parents.”
Indirect speech
What is indirect speech? we may have the substance of words used by the speaker and not his actual words. This is called indirect speech, in this reported is not put within inverted commas and does not begin with a capital letter. that has been placed before the indirect speech.
What are the examples of indirect speech?
He cried out joyfully that they had won.
The boy told the girl that he could hear her.
Leo asked his brother why he was crying.
Reporting and Reported speech
When the verb in one sentence reports, what is said by some speaker in another sentence in this sentence verb is called reporting verb , what is said in the second sentence is known as Reported speech.
Reporting speech : My sister said,
Reported speech : “It is time to go away.”
During the changing of the sentence Direct into indirect speech the personal pronouns and tense of the verbs in the reported speech undergo certain changes.
Rules for direct indirect speech
First person in the reported speech :
Direct: she says to me, “I am tired”
Indirect: She tells me that she is tired.
Direct: He said to me, “I am innocent”.
Indirect: He told me that he was innocent.
From the Discussion of the foregoing examples we learn:
- Each new character’s speech starts on a new line.
- A reporting clause is used at the end ( said hone, shouted Paul, replied mum).
- Speech is opened with speech marks.
- the line of the speech end with a comma, exclamation marks
- Verb tenses usually shift back a tense ( into the past)
- Words indicating place and time need to change.
- Pronoun often need to change.
Direct indirect speech Examples with PDF
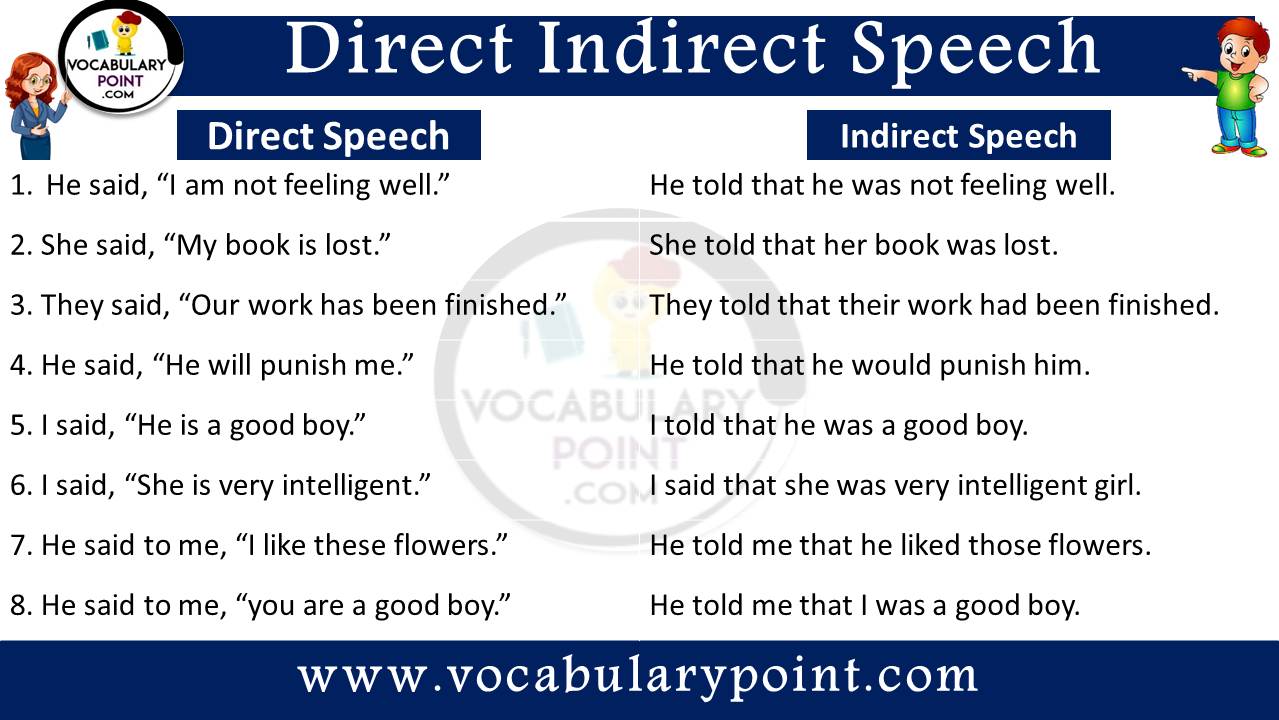
- He said, “I am not feeling well.”
He told that he was not feeling well.
- She said, “My book is lost.”
She told that her book was lost.
- They said, “Our work has been finished.”
They told that their work had been finished.
- He said, “He will punish me.”
He told that he would punish him.
- I said, “He is a good boy.”
I told that he was a good boy.
- I said, “She is very intelligent.”
I said that she was very intelligent girl.
- Aslam said, “They are my friends.”
Aslam told that they were his friends.
- He said to me, “I like these flowers.”
He told me that he liked those flowers.
- He said to me, “you are a good boy.”
He told me that I was a good boy.
- He said to us, “you are a good boy.”
He told to us that we were good boy.
- I said to her, “You are a clever girl.”
I told to her that she was a clever girl.
- We said to them, “you are making a noise.”
We told them that they were making a noise.
- I said to him, “You are not working hard.”
I told him that he was not working hard.
- I said to him, “I will help you.”
I told him that I would help him.
- He says to me, “I can kill you.”
He tells me that he can kill me.
- I say to her, “I shall see you tomorrow.”
I tell her that I shall see her tomorrow.
- He said to me, “I am your brother.”
He told me that he was my brother.
- We said to her, “Your English is very weak.
We told her that her English was very weak.
- I said to him, “Your book has been stolen.”
I told him that his book had been stolen.
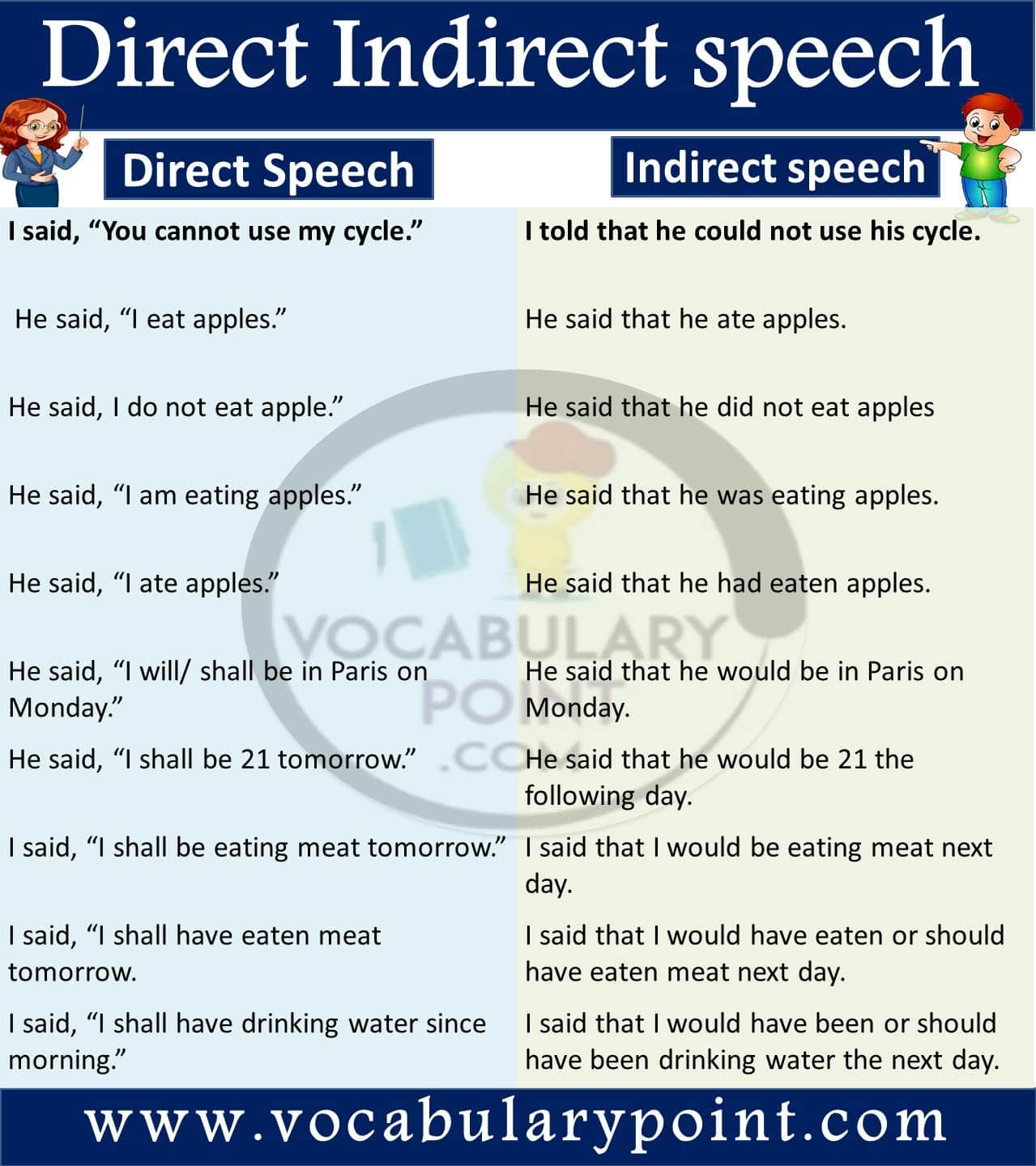
- I said, “You cannot use my cycle.”
I told that he could not use his cycle.
- He said, “I eat apples.”
He said that he ate apples.
- He said, I do not eat apple.”
He said that he did not eat apples.
- He said, “I am eating apples.”
He said that he was eating apples.
- He said, “I ate apples.”
He said that he had eaten apples.
- He said, “I will/ shall be in Paris on Monday.”
He said that he would be in Paris on Monday.
- He said, “I shall be 21 tomorrow.”
He said that he would be 21 the following day.
- I said, “I shall be eating meat tomorrow.”
I said that I would be eating meat next day.
- I said, “I shall have eaten meat tomorrow.
I said that I would have eaten or should have eaten meat next day.
- I said, “I shall have drinking water since morning.”
I said that I would have been or should have been drinking water the next day.
- He said, “I saw her a day before yesterday.”
He said that he had seen her two days before.
- He said, “I will do it tomorrow.”
He said that he would do it the next day.
- She said, I “My father died a year ago.”
She said that her father had died a year before/previous year.
- At the station, he said, “I shall be here again tomorrow.”
He said that he would be there again the next day.
- She said, “You can sit here, Saleem.”
She told saleem that he could sit beside her.
- He said, “Come here, boys.”
He called the boys.
Direct Indirect speech with examples and rules PDF
- He says to me, I am your friend.”
He tells me that he is my friend.
- I shall say, “You can help me.
I shall say that you can help me.
- You will say to me, “I have already gone to Lahore.”
You will tell me that you have already gone to Lahore.
- We say to her, “You know him.”
We tell her that she knows her.
- I shall say to him, “You were eating apples.”
I shall tell him that he was eating apples.
- He says, “We might go to Karachi.”
He says that they might go to Karachi.
- She says, “We had already seen this film.”
She says that they had already seen that him.
- He said to me, “I am ill.”
He told me that he was ill.
- I said, “I live in a good house.”
I said that I lived in a good house.
- She said, “I do not like boiled eggs.
She said that she did not like boiled eggs.
- I said to him, “I am playing cricket these days.”
I told him that I was playing cricket these days.
- I said to him, “I have done my duty.”
I told him that I had done my duty.
- The mother said to her son, “We have been living in this house since 1990.”
The mother told her son that they had been living in that house since1990.
- She said, “I was sick since yesterday.”
She said that she had been sick since previous day.
- The teacher said to the boys, “We cleaned the room a day ago.”
The teacher told the boys that they had cleaned the room a day before.
- I said to him, “I did not feel happy today.”
I told him that I had not felt happy that day.
- She said, “I had already cooked food for you.”
She said that she had already cooked for him.
- The doctor said, “I had been treating the patient for ten years.”
The doctor said that he had been treating the patient for ten years.
- The teacher said, “Each moves round the sun.”
The teacher said that earth moves round the sun.
- He said to me, “I shall go to college tomorrow.”
He told me that he would go to college the next day.
- He said to me, “It will be raining tomorrow.”
He told me that she it would be raining the next day.
- The Mother said to me, “I shall have done my duty.”
The mother told me that she would have done her duty.
- He said to me, “I shall have been doing my work.”
He told me that he would have been doing his work.


You can download PDF of Direct Indirect Speech with examples and Info graphics