List Of Mathematics Symbols With Name is a figure or a character that is used to represent a concept, an object, a number, or a data set. Symbols can represent basic operations, such as addition and multiplication, and more complex concepts, such as integrals and limits. In some cases, multiple symbols may be used to represent a single concept. For example, the equality symbol “=” can be read as “is equal to” or “is equivalent to.
What are Math Symbols?
Math symbols are the symbols used in mathematical notation to represent numbers, operations, relationships, and functions. They are essential for conveying mathematical concepts and equations succinctly and precisely. Here are some common categories and examples of math symbols:
- Numbers and Constants:
- Digits (0-9)
- Pi (π): Represents the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
- Euler’s Number (e): The base of natural logarithms, approximately equal to 2.71828.
- Basic Arithmetic Operations:
- Plus (+): Addition.
- Minus (−): Subtraction or negative sign.
- Multiply (× or *): Multiplication.
- Divide (÷ or /): Division.
- Advanced Operations:
- Square root (√): Represents the square root of a number.
- Exponentiation (^ or **): Indicates that one number is raised to the power of another.
- Factorial (!): Product of all positive integers up to a given number.
- Algebraic Symbols:
- Variables (like x, y, z): Represent unknown or variable quantities.
- Equals (=): Indicates equality.
- Plus-minus (±): Represents a number’s positive and negative values.
- Geometry:
- Angle (θ or ∠): Represents an angle.
- Parallel (‖): Indicates parallel lines.
- Perpendicular (⊥): Indicates perpendicular lines.
- Calculus:
- Integral (∫): Represents integration.
- Differential (d/dx): Denotes differentiation.
- Limit (lim): Represents the limit of a function.
- Set Theory:
- Union (∪): Represents the union of sets.
- Intersection (∩): Represents the intersection of sets.
- Subset (⊆): Indicates one set is a subset of another.
- Logic:
- And (∧): Logical conjunction.
- Or (∨): Logical disjunction.
- Not (¬): Logical negation.
- Probability and Statistics:
- Mean (µ): Represents the mean or average.
- Standard Deviation (σ): Indicates the standard deviation.
- Summation (Σ): Represents the sum of a sequence of numbers.
Must Learn:
Math Vocabulary Words
Mathematics symbols
Short Form of Words for Texting
Short Form of words used in chatting
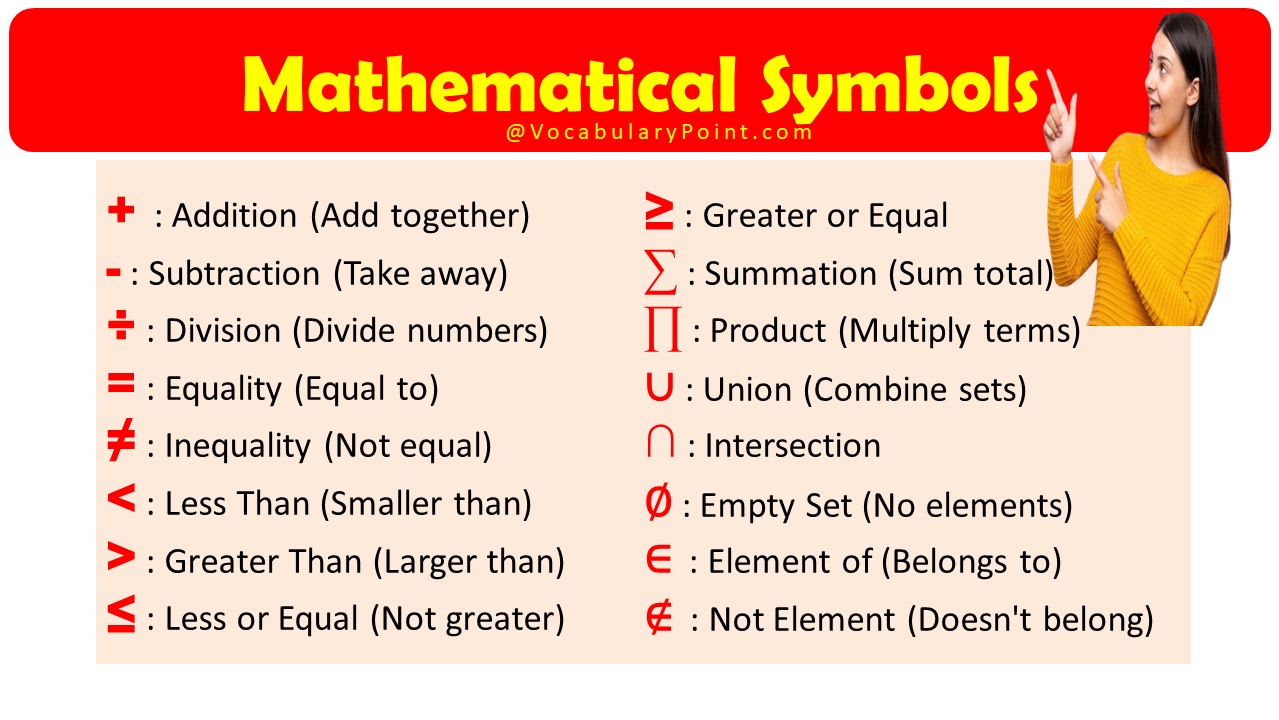
Mathematical Symbols With Names
- + : Plus
- − : Minus
- × : Times
- ÷ : Divided by
- = : Equals
- ≠ : Not equal
- ≈ : Approximately equal
- < : Less than
- > : Greater than
- ≤ : Less than or equal to
- ≥ : Greater than or equal to
- ! : Factorial
- √ : Square root
- ∑ : Summation
- ∏ : Product
- ∫ : Integral
- ∂ : Partial derivative
- ∞ : Infinity
- ∈ : Element of
- ∉ : Not an element of
- ∀ : For all
- ∃ : There exists
- ∅ : Empty set
- ∩ : Intersection
- ∪ : Union
- ⊂ : Subset of
- ⊃ : Superset of
- ⊆ : Subset of or equal to
- ⊇ : Superset of or equal to
- → : Implies
- ↔ : If and only if
- ∧ : And
- ∨ : Or
- ¬ : Not
- ℕ : Natural numbers
- ℤ : Integers
- ℚ : Rational numbers
- ℝ : Real numbers
- ℂ : Complex numbers
- α : Alpha
- β : Beta
- γ : Gamma
- δ : Delta
- ε : Epsilon
- ζ : Zeta
- η : Eta
- θ : Theta
- ι : Iota
- κ : Kappa
- λ : Lambda
- μ : Mu
- ν : Nu
- ξ : Xi
- ο : Omicron
- π : Pi
- ρ : Rho
- σ : Sigma
- τ : Tau
- υ : Upsilon
- φ : Phi
- χ : Chi
- ψ : Psi
- ω : Omega
- Γ : Gamma function
- Δ : Delta (difference or change)
- Θ : Theta function
- Λ : Lambda (wavelength)
- Ξ : Xi function
- Π : Product capital pi
- Σ : Capital sigma (summation)
- Υ : Upsilon (displacement)
- Φ : Phi (magnetic flux)
- Ψ : Psi function
- Ω : Omega (resistance)
- ∠ : Angle
- ° : Degree
- ′ : Prime (minutes, feet)
- ″ : Double prime (seconds, inches)
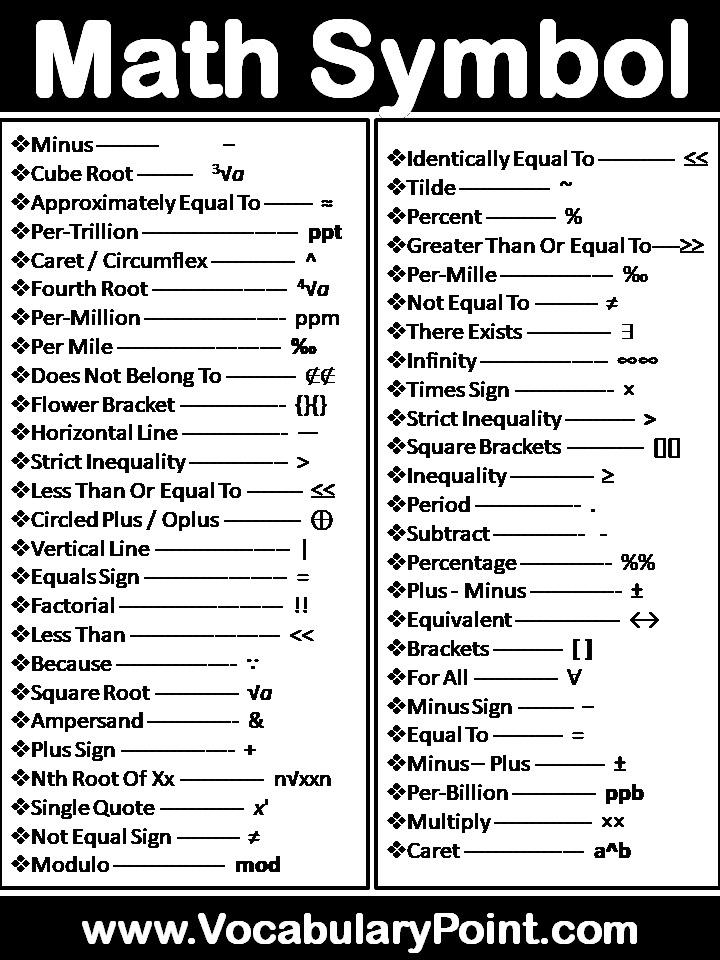
- ∵ : Because
- ∴ : Therefore
- ∼ : Tilde (similar to)
- ≡ : Identical to
- ≢ : Not identical to
- ≪ : Much less than
- ≫ : Much greater than
- ⊕ : Circled plus (direct sum)
- ⊖ : Circled minus
- ⊗ : Circled times
- ⊘ : Circled division slash
- ⊙ : Circled dot operator
- ⊛ : Circled asterisk operator
- ⊝ : Circled dash
- ⊞ : Squared plus
- ⊟ : Squared minus
- ⊠ : Squared times
- ⊡ : Squared dot operator
- ⊢ : Turnstile right tack
- ⊣ : Turnstile left tack
- ⊤ : Tack up
- ⊥ : Perpendicular
- ⊨ : Models
- ⊩ : Forces
- ⊪ : Triple bar
- ⊻ : Logical or
- ⊼ : Nand
- ⊽ : Nor
- ⋀ : N-ary logical and
- ⋁ : N-ary logical or
- ⋂ : N-ary intersection
- ⋃ : N-ary union
- ⋄ : Diamond operator
- ⋅ : Dot product
- ⋆ : Star operator
- ⋈ : Bowtie
- ⋉ : Left normal factor semidirect product
- ⋊ : Right normal factor semidirect product
- ⋋ : Left semidirect product
- ⋌ : Right semidirect product
- ⋍ : Reversed tilde equals
- ⋎ : Reversed tilde operator
- ⋏ : Logical nand
- ⋐ : Larger than or equal to
- ⋑ : Smaller than or equal to
- ⋒ : Double intersection
- ⋓ : Double union
List Of Mathematics Symbols With Name | Images
Basic Symbols of Mathematics
- + : Plus (Addition)
- − : Minus (Subtraction)
- × : Times (Multiplication)
- ÷ : Divided by (Division)
- = : Equals
- ≠ : Not Equal
- < : Less Than
- > : Greater Than
- ≤ : Less Than or Equal To
- ≥ : Greater Than or Equal To
- ! : Factorial
- √ : Square Root
- π : Pi (Approximately 3.14159)
- ∑ : Summation
- ° : Degree (used in angles and temperatures)
- ∞ : Infinity
- ∫ : Integral
- ∆ : Delta (Change/Difference)
- ∈ : Element Of (used in set theory)
- ∪ : Union (used in set theory)
- ∩ : Intersection (used in set theory)
- ∀ : For All (universal quantification)
- ∃ : There Exists (existential quantification)
- ∴ : Therefore
- ∵ : Because
List Of Math Symbols And Their Meanings
- + : Plus – Addition operation.
- − : Minus – Subtraction operation.
- × : Times – Multiplication operation.
- ÷ : Divided by – Division operation.
- = : Equals – Indicates equality.
- ≠ : Not equal – Indicates inequality.
- < : Less than – Comparison operator indicating less than.
- > : Greater than – Comparison operator indicating greater than.
- ≤ : Less than or equal to – Indicates less than or equal.
- ≥ : Greater than or equal to – Indicates greater than or equal.
- ! : Factorial – Product of all positive integers up to a given number.
- √ : Square root – Principal square root of a number.
- π (Pi) : Represents the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, approximately 3.14159.
- ∑ : Summation – Sum of a sequence of numbers.
- ° : Degree – Unit of angle measurement.
- ∞ : Infinity – Concept of something without any limit.
- ∫ : Integral – Represents integration in calculus.
- ∆ (Delta) : Change/Difference – Commonly used to denote a change in a variable.
- ∈ : Element of – Signifies an element in a set.
- ∪ : Union – Represents the union of two sets.
- ∩ : Intersection – Represents the intersection of two sets.
- ∀ : For all – Universal quantification, applicable to all instances.
- ∃ : There exists – Existential quantification, something exists.
- ∴ : Therefore – Denotes a logical consequence.
- ∵ : Because – Indicates a reason or cause.