we’re going to explore the wonderful world of Nature And Environment Vocabulary. Nature is all around us, from the towering trees in the forest to the tiny insects buzzing in the garden. By learning nature vocabulary, we can better understand and appreciate the beauty of the world around us. Whether you’re a curious kid, a diligent student, or an English learner looking to expand your vocabulary, you’re in the right place! Let’s dive into the enchanting realm of nature together and discover some fascinating words along the way.
Nature Vocabulary
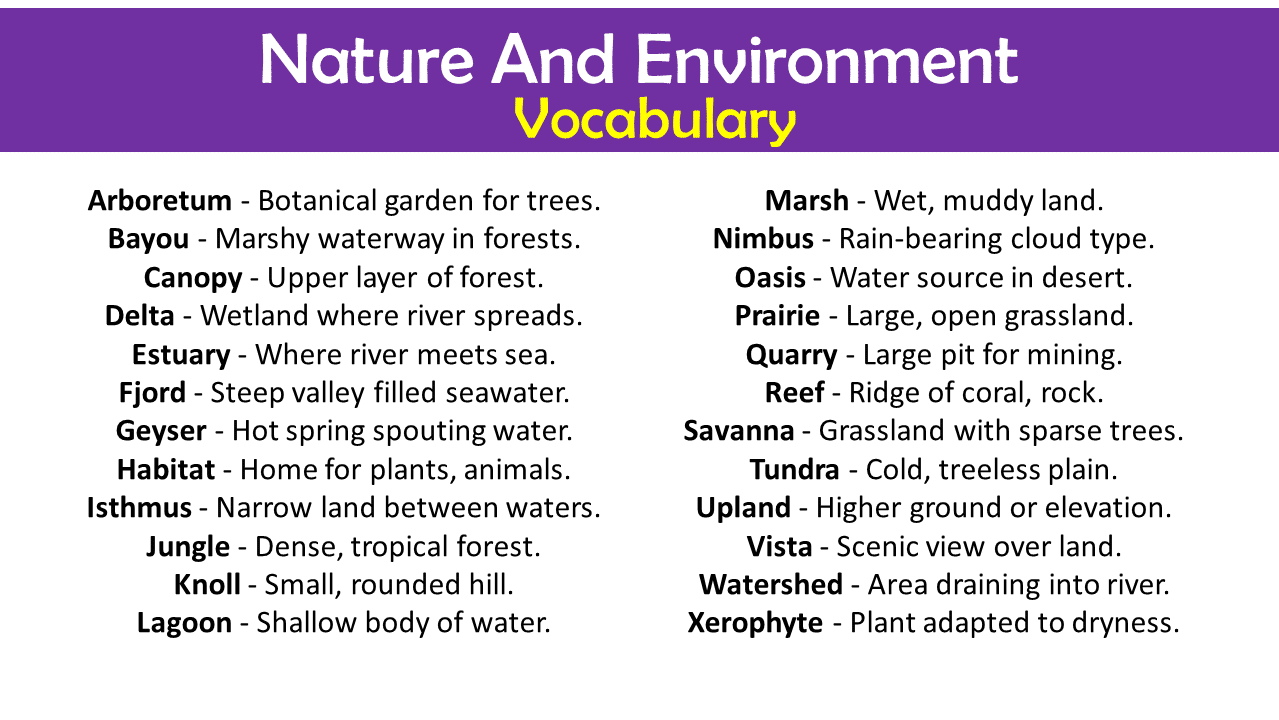
- Arboretum – Botanical garden for trees.
- Bayou – Marshy waterway in forests.
- Canopy – Upper layer of forest.
- Delta – Wetland where river spreads.
- Estuary – Where river meets sea.
- Fjord – Steep valley filled seawater.
- Geyser – Hot spring spouting water.
- Habitat – Home for plants, animals.
- Isthmus – Narrow land between waters.
- Jungle – Dense, tropical forest.
- Knoll – Small, rounded hill.
- Lagoon – Shallow body of water.
- Marsh – Wet, muddy land.
- Nimbus – Rain-bearing cloud type.
- Oasis – Water source in desert.
- Prairie – Large, open grassland.
- Quarry – Large pit for mining.
- Reef – Ridge of coral, rock.
- Savanna – Grassland with sparse trees.
- Tundra – Cold, treeless plain.
- Upland – Higher ground or elevation.
- Vista – Scenic view over land.
- Watershed – Area draining into river.
- Xerophyte – Plant adapted to dryness.
- Yucca – Desert plant, spiky leaves.
- Zephyr – Soft, gentle breeze.
- Butte – Isolated hill with steep sides.
- Creek – Small stream or brook.
- Dune – Hill of sand formed by wind.
- Evergreen – Plant that stays green year-round.
- Foliage – Leaves of a plant.
- Grove – Group of trees.
- Highland – Area of high land.
- Island – Land surrounded by water.
- Jetty – Structure extending into water.
- Kelp – Large seaweed.
- Loam – Fertile soil with clay/sand/silt.
- Meadow – Field with wild flowers.
- Nook – Secluded, sheltered place.
- Orchard – Area planted with fruit trees.
- Plateau – Area of flat highland.
- Quagmire – Soft boggy area.
- Rill – Small stream.
- Stream – Small river.
- Taiga – Boreal forest or snow forest.
- Undergrowth – Low-growing forest plants.
- Valley – Low area between hills.
- Wetland – Land consisting of marshes or swamps.
- Yardang – Ridge formed by wind erosion.
- Zenith – Highest point in the sky.
- Alpine – High mountains.
- Brook – Small stream.
- Chaparral – Dense vegetation of shrubs.
- Dew – Condensed moisture on surfaces.
- Ecotone – Transition area between ecosystems.
- Flora – Plant life of a region.
- Glacier – Large ice mass.
- Hillock – Small hill.
- Inlet – Small arm of the sea.
- Juniper – Evergreen shrub with berries.
- Kettle – Hole left by glaciers.
- Leaf – Flattened structure of plants.
- Mangrove – Tropical coastal vegetation.
- Narrows – Narrow passage of water.
- Outcrop – Visible rock formations.
- Pond – Small body of water.
- Quartz – Hard mineral, often crystalline.
- Ridge – Long narrow hilltop.
- Silt – Fine sand, clay, or soil.
- Thicket – Dense group of bushes.
- Umbra – Fully shaded inner region.
- Veld – Open grassland in Africa.
- Whirlpool – Water spinning rapidly.
- Xeric – Dry, desert-like conditions.
- Yield – Produce or provide naturally.
- Zooplankton – Small floating animals.
- Bloom – Flower or flowering.
- Cliff – Steep rock face.
- Driftwood – Wood washed ashore.
- Erosion – Wearing away by water/wind.

Nature And Environment Vocabulary
- Biodiversity – Variety of life forms.
- Biome – Large ecosystem type.
- Carbon footprint – Environmental impact measurement.
- Compost – Organic matter decomposition.
- Conservation – Protecting natural resources.
- Deforestation – Destruction of forests.
- Ecosystem – Interacting organisms and environment.
- Endangered – At risk of extinction.
- Fauna – Animal life of region.
- Flora – Plant life of region.
- Greenhouse gas – Atmosphere-warming emissions.
- Habitat – Natural home of species.
- Herbivore – Plant-eating animal.
- Invasive species – Disruptive non-native species.
- Keystone species – Crucial for ecosystem balance.
- Microclimate – Local area climate.
- Natural resource – Materials from Earth.
- Organic – Natural matter production.
- Ozone layer – Atmospheric UV shield.
- Photosynthesis – Plant sunlight energy conversion.
- Pollination – Transfer of pollen.
- Precipitation – Rain, snow, sleet, hail.
- Recycling – Reusing material.
- Renewable energy – Sustainable energy source.
- Sustainability – Long-term ecological balance.
- Topography – Land surface features.
- Toxic – Poisonous.
- Veganism – Avoiding animal products.
- Vegetation – Plant life collectively.
- Watershed – Drainage basin.
- Wetlands – Water-saturated land.
- Wildlife – Animals in natural environments.
- Wind energy – Power from wind.
- Xeriscaping – Drought-tolerant landscaping.
- Zero waste – Minimal waste lifestyle.
- Acid rain – Polluted, harmful rainwater.
- Biofuel – Fuel from organic materials.
- Carnivore – Meat-eating animal.
- Decomposer – Organism breaking down dead materials.
- Ecology – Study of organisms, environment.
Natural World Vocabulary
- Archipelago – Group of islands.
- Barren – Lacking plant life.
- Coral – Marine organisms’ limestone skeletons.
- Dell – Small, secluded valley.
- Elevation – Height above sea level.
- Fen – Low, marshy or flooded area.
- Grotto – Small picturesque cave.
- Heath – Open, uncultivated land.
- Igneous – Rock formed from magma.
- Jojoba – Desert shrub, oil-rich seeds.
- Kelpie – Water spirit in folklore.
- Loess – Wind-deposited silt or clay.
- Monsoon – Seasonal reversing wind/rain.
- Nectar – Sweet fluid in flowers.
- Orogeny – Mountain formation process.
- Peat – Decayed vegetable matter.
- Quicksand – Loose, wet sand that ensnares.
- Ravine – Deep, narrow gorge.
- Sedimentary – Rock formed from sediment.
- Terrace – Step-like landform.
- Unkempt – Wild, not maintained.
- Volcano – Opening in Earth’s crust.
- Wadi – Dry riverbed or valley.
- Xanthophyll – Yellow pigment in leaves.
- Yew – Evergreen tree, red berries.
- Zircon – Mineral, zirconium silicate.
- Anthropocene – Epoch dominated by humans.
- Bramble – Rough, prickly shrub.
- Coppice – Area with small tree growth.
- Drift – Movement of surface material.
- Escarpment – Long steep slope.
- Fluvial – Related to rivers.
- Gulch – Deep, narrow ravine.
- Humus – Organic component of soil.
- Isotherm – Line on map connecting equal temperature.
- Juxtapose – Place close together for contrasting.
- Katabatic – Wind flowing downhill.
- Lichen – Composite organism of algae and fungi.
- Mesa – Flat-topped hill with steep sides.
- Niche – Species’ role in ecosystem.