Figure of speech with examples refers to the artistic use of language to express ideas in a non-literal, imaginative way. For instance, a simile compares two things using “like” or “as,” as in “as brave as a lion.” Metaphors imply a comparison, like “time is a thief.” Hyperbole exaggerates for effect, such as “I’ve told you a million times.” These devices add depth and creativity to language.
What are Figures Of Speech?
Figures of speech are linguistic tools that writers and speakers use to convey ideas in a more vivid and imaginative way. They involve the use of words or phrases in a manner that differs from their usual literal interpretation to add emphasis, clarity, or freshness to expression.
Types of Figures of Speech
- Simile
- Metaphor
- Personification
- Hyperbole
- Understatement
- Metonymy
- Synecdoche
- Alliteration
- Assonance
- Onomatopoeia
- Irony
- Sarcasm
- Satire
- Oxymoron
- Paradox
- Pun
- Allusion
- Allegory
- Euphemism
- Anaphora
- Epistrophe
- Litotes
- Chiasmus
- Zeugma
- Apostrophe
- Antithesis
- Asyndeton
- Polysyndeton
- Synesthesia
- Tautology
Must learn: All Parts of speech
Figure of Speech With Examples

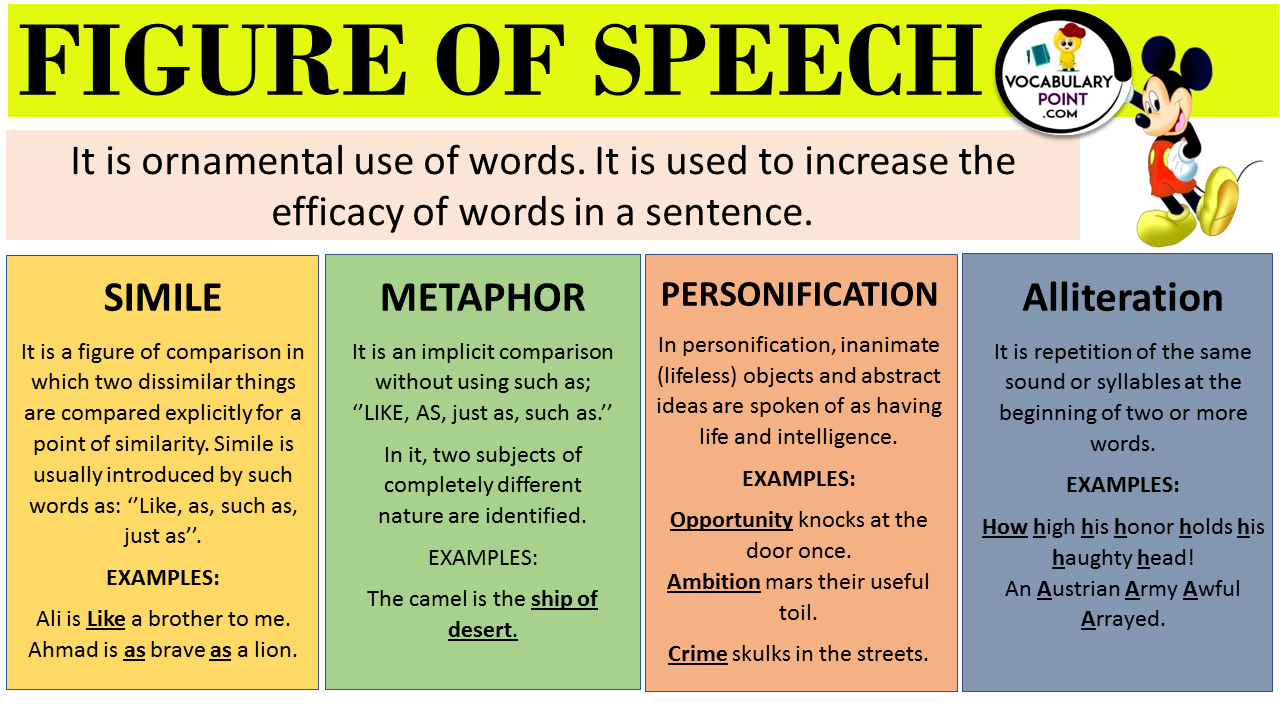
Simile
Definition: A simile compares two different things using “like” or “as.”
Examples:
- Quick as lightning
- Cold like ice
- Brave as a lion
- Sweet as sugar
- Sharp as a tack
Uses: Similes are used to make descriptions more vivid and engaging by drawing a comparison.
Metaphor
Definition: A metaphor directly compares two unrelated things without using “like” or “as.”
Examples:
- Time is money
- Heart of stone
- Life’s a journey
- Sea of troubles
- World’s a stage
Uses: Metaphors are used for a stronger impact to convey similarities in a more direct manner.
Personification
Definition: Personification gives human qualities to non-human entities.
Examples:
- Time marches on
- Wind whispers secrets
- Sun smiled down
- Trees danced in wind
- Stars winked in sky
Uses: Personification is used to add vividness to non-human elements, making descriptions more relatable and poetic.
Hyperbole
Definition: Hyperbole is an exaggerated statement or claim not meant to be taken literally.
Examples:
- I’m starving to death
- Cried a river
- Faster than the wind
- Tons of homework
- Sky-high prices
Uses: Hyperboles are used to add emphasis or express strong emotion.
Understatement
Definition: An understatement makes a situation seem less important or serious than it is.
Examples:
- Just a scratch
- Somewhat expensive
- Slightly chilly
- A bit uncomfortable
- Mildly interesting
Uses: Understatements are often used for ironic or humorous effect.
Metonymy
Definition: Metonymy is a figure of speech in which a thing or concept is referred to by something closely associated with it.
Examples:
- White House for President
- The pen for writing
- Hollywood for cinema
- Silicon Valley for tech
- The crown for royalty
Uses: Metonymy is used to provide a more concise or indirect reference.
Synecdoche
Definition: Synecdoche is where a part represents the whole or the whole represents a part.
Examples:
- Wheels for car
- Bread for food
- Hands for helpers
- Sails for ship
- Head for cattle
Uses: Synecdoche is used for stylistic effect, often in poetry and literature.
Alliteration
Definition: Alliteration is the repetition of the same initial consonant sounds in successive words.
Examples:
- Peter Piper picked
- Silly Sally swiftly
- Big bad bear
- Round the rugged rock
- Crazy cats clambered
Uses: Alliteration is used to create rhythm, enhance mood, and emphasize certain words.
Assonance
Definition: Assonance is the repetition of vowel sounds in nearby words.
Examples:
- Hollow and mellow
- Men sell the wedding bells
- The light of the fire
- Same game fame
- Trail and pain
Uses: Assonance is often used in poetry to create a particular mood or rhythm.
Onomatopoeia
Definition: Onomatopoeia is the use of words that imitate natural sounds.
Examples:
- Buzz of bees
- Hiss of snake
- Tick-tock of clock
- Sizzle of bacon
- Clap of thunder
Uses: Onomatopoeia is used to make descriptions more expressive and vivid.
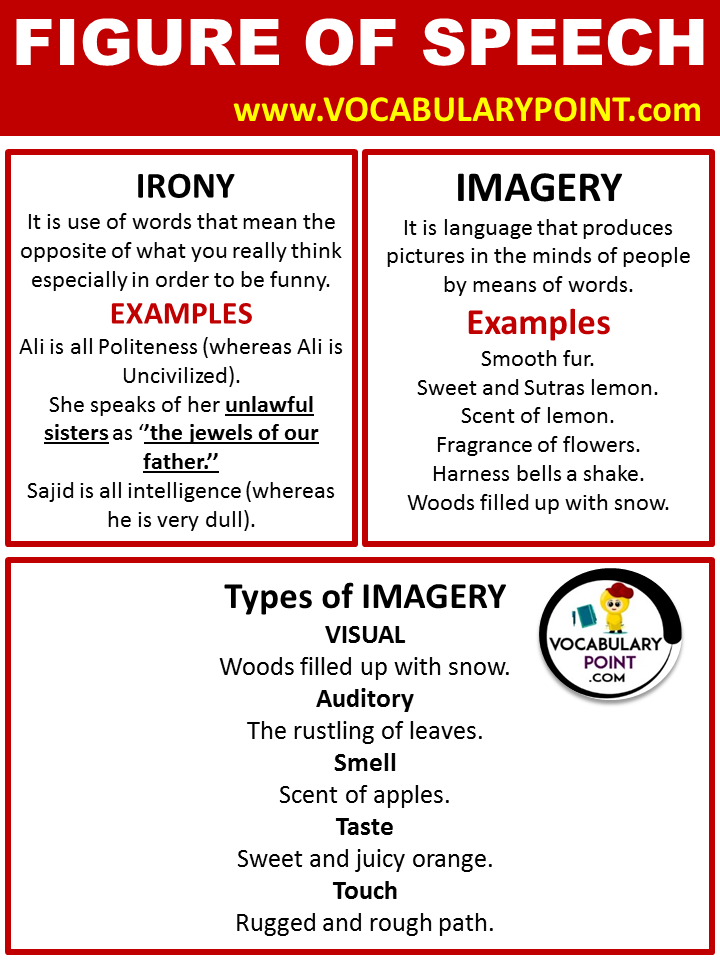
Irony
Definition: Irony involves words that are used in a way that their intended meaning is different from the actual meaning.
Examples:
- Clear as mud
- Bigger than a minute
- Awfully good
- Seriously funny
- Deafening silence
Uses: Irony is used to convey sarcasm or humor, or to emphasize the opposite of what is actually said.
Sarcasm
Definition: Sarcasm is a sharp, bitter, or cutting expression or remark; a bitter gibe or taunt.
Examples:
- Nice going, genius
- I’m not lazy, I’m relaxed
- What a pleasant surprise
- Thanks for the help, really
- I’m so thrilled
Uses: Sarcasm is often used for humor, criticism, or some form of wit.
Satire
Definition: Satire is the use of humor, irony, exaggeration, or ridicule to expose and criticize people’s stupidity or vices.
Examples:
- Political cartoons
- Parody news articles
- Comedic imitations
- Mockumentaries
- Ironic compliments
Uses: Satire is often used in literature, arts, and media to highlight societal or political issues.
Oxymoron
Definition: An oxymoron is a figure of speech in which apparently contradictory terms appear in conjunction.
Examples:
- Jumbo shrimp
- Deafening silence
- Seriously funny
- Bitter sweet
- Living dead
Uses: Oxymorons are used to create an effect of surprise or to emphasize a point through contradiction.
Paradox
Definition: A paradox is a statement that, despite apparently sound reasoning from true premises, leads to a self-contradictory or logically unacceptable conclusion.
Examples:
- I’m a liar
- Less is more
- Nobody goes there anymore; it’s too crowded
- This statement is false
- The only constant is change
Uses: Paradoxes are often used to provoke thought or illustrate a point about the complexity of reality.
Pun
Definition: A pun is a play on words in which a humorous effect is produced by using a word that suggests two or more meanings.
Examples:
- A horse is a stable animal
- Time flies like an arrow; fruit flies like a banana
- I used to be a baker, but I couldn’t make enough dough
- I’m reading a book on anti-gravity, it’s impossible to put down
- An eggcellent idea
Uses: Puns are used to create humor and are often found in literature and everyday conversation.
Allusion
Definition: An allusion is a brief and indirect reference to a person, place, thing, or idea of historical, cultural, literary, or political significance.
Examples:
- He’s a real Romeo
- It’s her Achilles’ heel
- Don’t act like a Scrooge
- A Pandora’s box of problems
- He has a Herculean task
Uses: Allusions are used to enrich a text by drawing on the knowledge and associations of the reader, often to create deeper meanings.
Allegory
Definition: An allegory is a narrative in which characters and events represent broader themes and concepts.
Examples:
- Animal Farm: political allegory
- The Tortoise and Hare: moral allegory
- Plato’s Cave: philosophical allegory
- The Lion, the Witch, and the Wardrobe: religious allegory
- Lord of the Flies: societal allegory
Uses: Allegories are used to convey complex ideas and themes through symbolic figures, actions, or imagery.
Euphemism
Definition: A euphemism is a mild or indirect word or expression substituted for one considered to be too harsh or blunt.
Examples:
- Passed away: died
- Between jobs: unemployed
- Economically disadvantaged: poor
- Collateral damage: civilian deaths
- Letting you go: fired
Uses: Euphemisms are used to soften the impact of difficult or sensitive subjects.
Anaphora
Definition: Anaphora is the repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of successive clauses.
Examples:
- We shall fight, we shall win
- Every child, every teacher, every parent
- To think, to dream, to believe
- No pain, no gain, no glory
- Freedom for all, justice for all
Uses: Anaphora is used to emphasize a point and create a rhythm and appeal in speech or writing.
Epistrophe
Definition: Epistrophe is the repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive clauses.
Examples:
- See no evil, hear no evil
- Government of the people, by the people, for the people
- Born to be wild, live to be wild
- I swear to tell the truth, the whole truth
- Lost time, lost opportunities, lost dreams
Uses: Epistrophe is used for emphasis and to create a rhythmical and eloquent effect.
Litotes
Definition: Litotes is a figure of speech that employs an understatement by using double negatives.
Examples:
- Not too bad: good
- Not a bad idea: good idea
- Not unfamiliar: familiar
- She’s not unattractive: attractive
- It’s not rocket science: simple
Uses: Litotes is used to provide emphasis, create irony, or soften the impact of a statement.
Chiasmus
Definition: Chiasmus is a rhetorical device in which two or more clauses are balanced against each other by the reversal of their structures.
Examples:
- Never let a fool kiss you
- Ask not what your country
- You forget what you want
- Bad men live that they
- She has all my love
Uses: Chiasmus is used to create a memorable impact and often used in speeches for emphasis.
Zeugma
Definition: Zeugma is a figure of speech where a word applies to multiple parts of the sentence.
Examples:
- Lost his coat and temper
- He opened his mind and wallet
- She broke his car and heart
- He caught a fish and cold
- Left in anger and haste
Uses: Zeugma is used for stylistic effect to create surprise or humor.
Apostrophe
Definition: An apostrophe is a figure of speech in which a speaker directly addresses an absent person or a personified quality, object, or idea.
Examples:
- O Death, where is thy sting?
- Twinkle, twinkle, little star
- Hello darkness, my old friend
- Roll on, thou deep and dark
- O Time, thou must untangle
Uses: Apostrophes are used for dramatic effect or to convey deep emotions.
Antithesis
Definition: Antithesis is a rhetorical device in which two opposite ideas are put together in a sentence to achieve a contrasting effect.
Examples:
- Speech is silver, silence gold
- One small step, giant leap
- To err is human, to forgive divine
- Better late than never, but never late
- You are easy on the eyes, but hard on the heart
Uses: Antithesis is used to create a stark contrast between two ideas or concepts, highlighting the difference.
Asyndeton
Definition: Asyndeton is a writing style where conjunctions are omitted in a series of words, phrases, or clauses.
Examples:
- I came, I saw, I conquered
- Without warning, without reason, without mercy
- Government of the people, by the people, for the people
- We shall pay any price, bear any burden, meet any hardship
- Reduce, reuse, recycle
Uses: Asyndeton is used to create a concise, impactful, and dramatic effect.
Polysyndeton
Definition: Polysyndeton is the use of several conjunctions in close succession, especially where they are usually replaced by commas.
Examples:
- And we laughed and played and talked
- There were fountains and gardens and trees
- They read and studied and wrote and drilled
- He was tall and strong and brave and wise
- It’s all or nothing, now or never, do or die
Uses: Polysyndeton is used to create a feeling of overwhelming abundance or continuous sequence.
Synesthesia
Definition: Synesthesia is a figure of speech in which one sense is described using terms from another.
Examples:
- Loud colors
- Bitter cold
- Sweet sound
- Warm aroma
- Silky voice
Uses: Synesthesia is used to blend the senses in descriptions, creating vivid and unexpected imagery.
Tautology
Definition: Tautology is the repetitive use of phrases or words which have similar meanings.
Examples:
- Free gift
- Added bonus
- Past history
- Safe haven
- Unexpected surprise
Uses: Tautology is often used unintentionally but can be employed for emphasis or clarity.