Conjunctions are fundamental components of English grammar, acting as connectors between words, phrases, or clauses. They are crucial for creating complex sentences and conveying clear, coherent ideas. Broadly categorized into coordinating, subordinating, and correlative types, each type of conjunction serves a specific purpose in enhancing the flow and clarity of language.
What are Conjunctions?
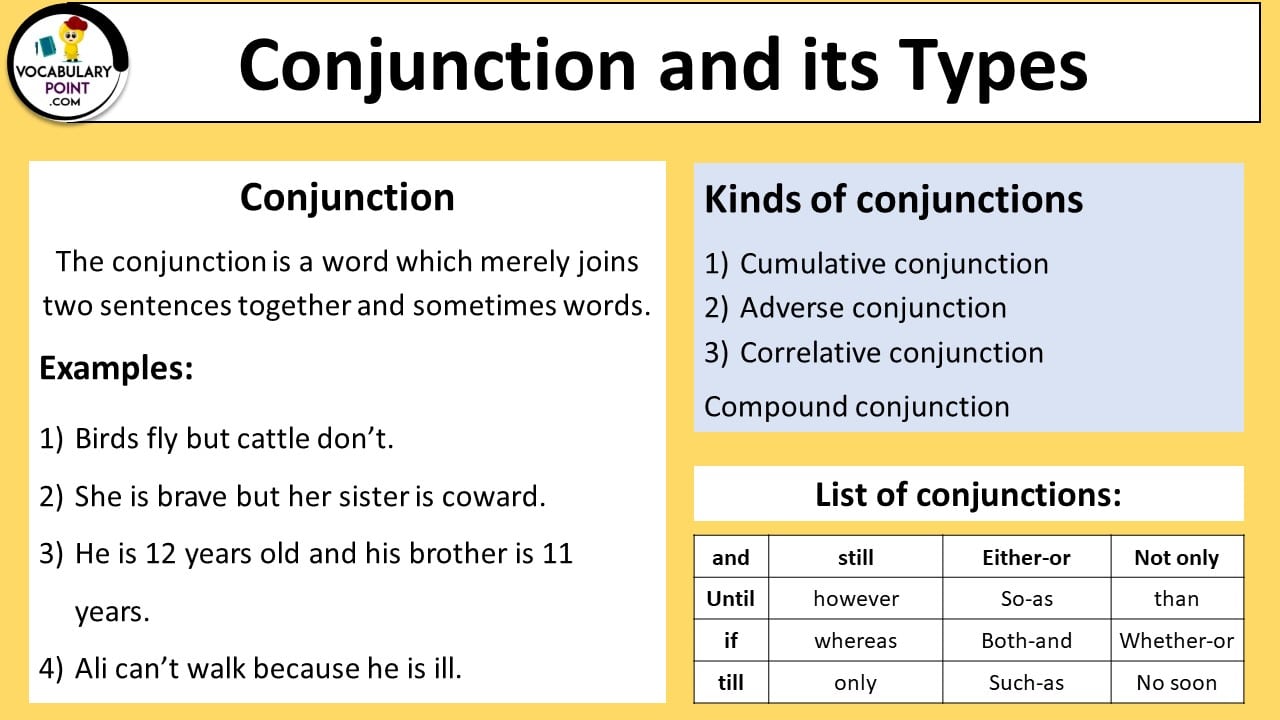
Definition: Conjunctions are words that connect clauses, sentences, words, or phrases in a sentence. They are an essential part of English grammar, providing fluidity and coherence to writing and speech. Conjunctions help in forming complex and compound sentences and can express various relationships between ideas, such as addition, contrast, cause, and condition.
Conjunction and its Types
Conjunctions are categorized based on their function and the way they connect elements in a sentence. Different types of conjunctions serve different purposes, ranging from adding information to showing contrast or cause-and-effect relationships.
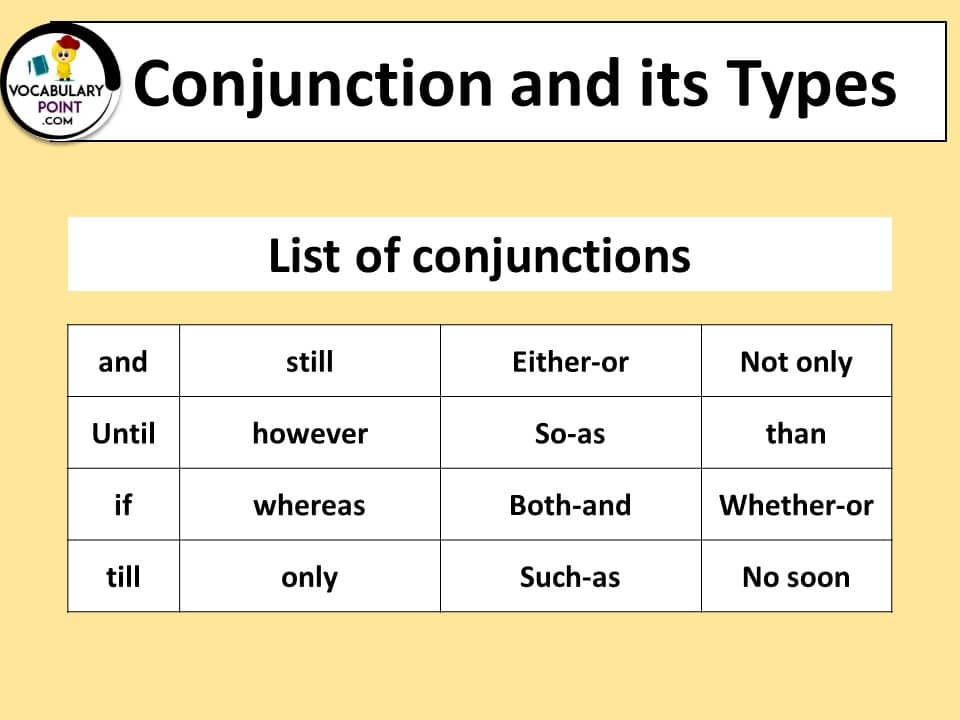
All Types of Conjunctions:
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions connect words, phrases, or independent clauses of equal importance or similar grammatical structure.
- Examples in Sentences:
- I want to eat pizza and
- She must leave now or she will miss her flight.
- He tried hard but he failed the exam.
- She is smart yet
- I was tired, so I went to bed early.
- Neither the rain nor the cold bothered them.
- Not only did he apologize, but he also offered a refund.
- You can either stay here or come with us.
- I like both tea and
- He can neither read nor
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions connect a dependent clause to an independent clause, showing a relationship like cause, time, or condition.
- Examples in Sentences:
- I will go to the park if it doesn’t rain.
- Although she was tired, she finished the marathon.
- We can start dinner as soon as you get home.
- He passed the exam because he studied hard.
- Unless you apologize, I won’t forgive you.
- While I was shopping, the phone rang.
- She was happy even though she didn’t win.
- Since you are here, let’s start the meeting.
- He couldn’t see anything, as it was too dark.
- Whenever I call, she is busy.
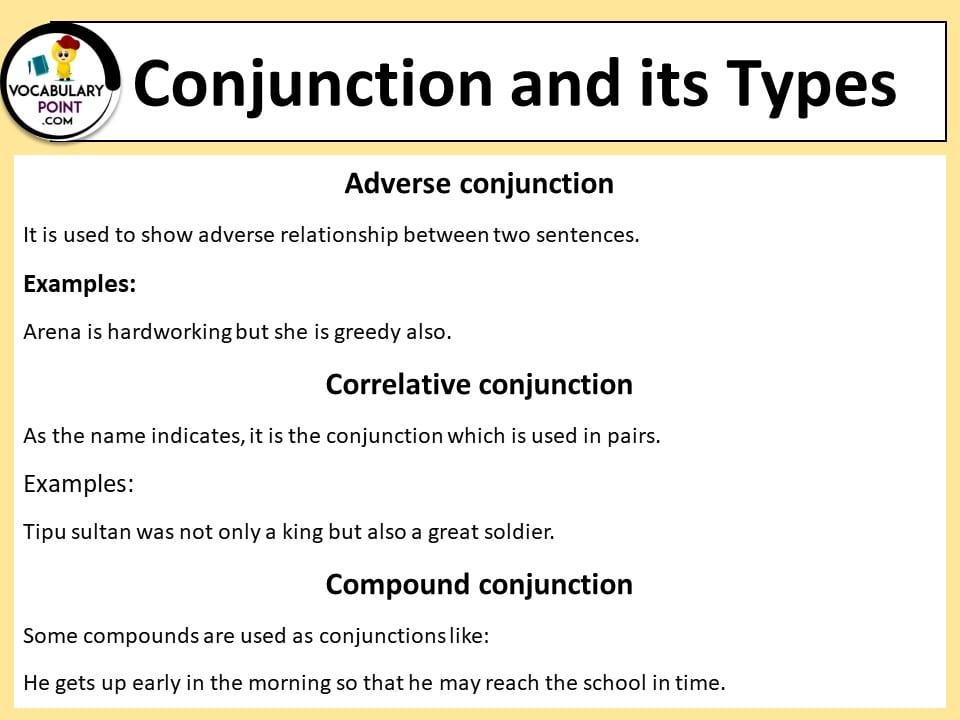
Correlative Conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions are pairs of conjunctions that work together to connect elements in a sentence.
- Examples in Sentences:
- Both the cake and the pie are delicious.
- She will either go to Paris or
- Neither the red shirt nor the blue shirt fits me.
- Not only is he smart, but he is also kind.
- You can either stay or
- Whether you like it or not, you have to go.
- She is both intelligent and
- Not only do they sing, but they also dance.
- As much as I like you, I cannot agree.
- No sooner had I arrived than it started raining.
Must Learn About:
Nouns, Pronouns, Verbs, Adjectives, Adverbs, Interjections, Prepositions, Conjunctions
Comparative Conjunctions
Definition: Comparative conjunctions are used to compare two clauses, indicating how one is related to the other in terms of similarity or difference. These conjunctions often involve comparisons using “as…as,” “than,” or “so…as.”
- Examples in Sentences:
- He is as tall as his brother.
- She sings better than she dances.
- The book was not so interesting as the movie.
- This car is more expensive than that one.
- He is just as clever as she is.
- The dessert was less appealing than the appetizer.
- She is equally skilled as her teammate.
- The test was easier than I expected.
- He works harder than his colleagues.
- The sequel was not as exciting as the original film.
Concessive Conjunctions
Definition: Concessive conjunctions are used to express a contrast or concession, showing that one clause is surprising or unexpected in relation to another. Words like “although,” “though,” and “even though” are common concessive conjunctions.
- Examples in Sentences:
- Although it rained, the event was successful.
- She passed the test, even though she didn’t study much.
- Though he was late, he didn’t miss anything important.
- He enjoyed the movie, despite its poor reviews.
- While she is a great athlete, she excels academically too.
- Even if it’s cold, I will go for a walk.
- Despite feeling ill, he went to work.
- Whereas he loves adventure, she prefers quiet evenings.
- No matter how hard it is, she never gives up.
- Regardless of the risk, they proceeded with the plan.
Conditional Conjunctions
Definition: Conditional conjunctions introduce conditions, often indicating that one event depends on another. They include words like “if,” “unless,” and “provided that.”
- Examples in Sentences:
- If it rains, we will cancel the trip.
- You can go out provided that you finish your homework.
- Unless you apologize, she won’t forgive you.
- He’ll be happy if he gets a promotion.
- You can succeed as long as you work hard.
- Supposing that she agrees, what will you do next?
- In case it gets cold, bring a jacket.
- Even if it’s difficult, keep trying.
- You’ll win provided that you play well.
- If you study, you will pass the exam.
Causal Conjunctions
Definition: Causal conjunctions are used to show the cause-and-effect relationship between two clauses. They include conjunctions like “because,” “since,” and “as.”
- Examples in Sentences:
- I’m tired because I didn’t sleep well.
- He succeeded since he worked hard.
- As she was ill, she stayed at home.
- She was late due to heavy traffic.
- They won the match because of their teamwork.
- Since it’s raining, we’ll stay indoors.
- As he’s not here, we’ll start without him.
- Owing to the storm, the event was postponed.
- She’s upset because she lost her keys.
- Due to unforeseen circumstances, the meeting is canceled.
Temporal Conjunctions
Definition: Temporal conjunctions are used to denote time, indicating when something happens. They include “when,” “while,” “before,” “after,” and “until.”
- Examples in Sentences:
- When I arrived, the meeting had already started.
- He called while I was cooking.
- Before you leave, turn off the lights.
- After the movie, we went for dinner.
- Wait here until I return.
- While she was reading, the phone rang.
- As soon as he arrived, they began the presentation.
- She finished her work before going to bed.
- Once he understands the rules, he’ll play better.
- Until you apologize, I won’t speak to you.
Conjunctions of Manner
Definition: Conjunctions of manner indicate the manner or way in which something is done. They include “as,” “like,” and “as if.”
- Examples in Sentences:
- Do it as I showed you.
- She sings like a professional.
- It seemed as if the world had stopped.
- He acts as though he owns the place.
- She speaks like she knows everything.
- Work as if your life depends on it.
- He ran as though being chased.
- She treated him like a child.
- It looks as if it might rain.
- Behave as a responsible adult.
Disjunctive or Alternative Conjunctions
Definition: Disjunctive or alternative conjunctions offer choices or alternatives between words, phrases, or clauses. They include “or,” “either…or,” and “neither…nor.”
- Examples in Sentences:
- Do you want tea or coffee?
- You can either stay here or come with me.
- Neither the red shirt nor the blue one fits me.
- She will either accept the job or decline it.
- Neither John nor Mary was at the party.
- You can either cook or order food.
- He is interested in neither science nor
- We can go either today or
- Either you apologize or
- Neither a borrower nor a lender be.
30 Examples of Conjunctions in Sentences
- We can go to the beach or the park.
- He is smart but
- She likes to read books and
- Although it was raining, we had fun.
- You must hurry or you’ll be late.
- She will succeed because she works hard.
- Unless you study, you won’t pass.
- He is tired yet he keeps working.
- As it was late, we left.
- While I was cooking, the phone rang.
- Both the cat and the dog are sleeping.
- Either you leave now or you stay till the end.
- Neither John nor Mary came to the party.
- He is not only talented but also
- We will go whether it rains or not.
- Since you asked, I’ll tell you.
- If you call me, I will answer.
- I like her because she is kind.
- Though he’s young, he’s very mature.
- Even though it’s cold, I will go for a walk.
- Whenever I see you, I smile.
- He finished his work so he could relax.
- No sooner had she arrived than she had to leave.
- I’ll join you as soon as I’m ready.
- She can either cook or order food.
- Not only is he a good teacher, but he’s also a great mentor.
- We stayed inside because it was raining.
- Though it was difficult, she completed the task.
- You must decide whether to stay or
- As much as I like the beach, I prefer the mountains.
Download PDF

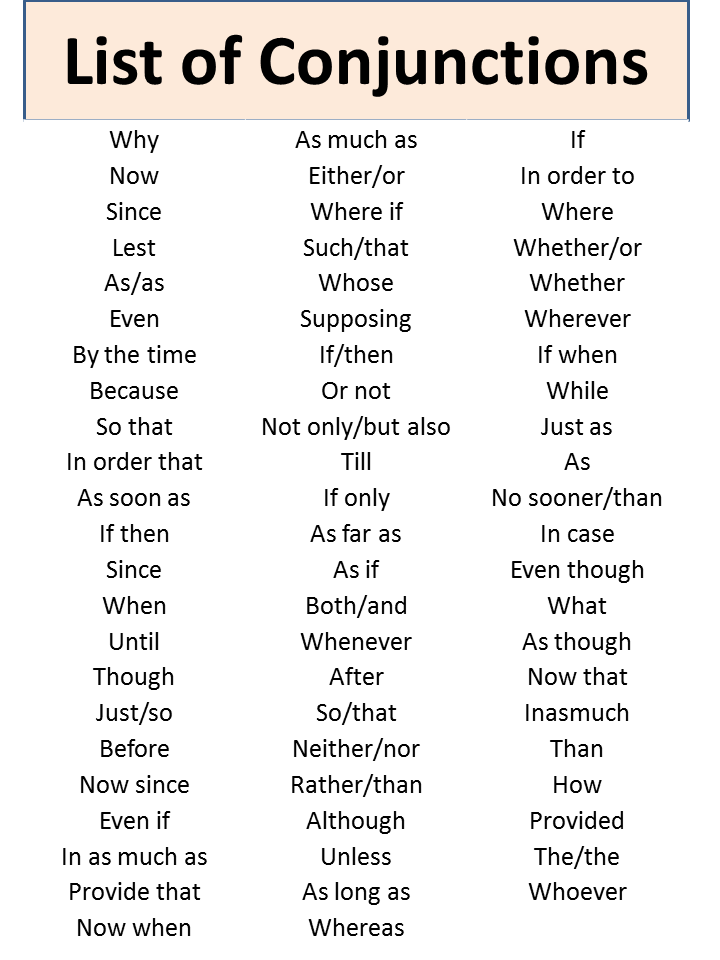
List of Conjunctions
Coordinating Conjunctions:
- And
- But
- Or
- Nor
- For
- Yet
- So
Subordinating Conjunctions:
- Although
- As
- Because
- Before
- If
- Once
- Since
- Though
- Until
- When
- Where
- While
- After
- Unless
- Whereas
- Whenever
- Even though
- As if
- As long as
- As much as
- As soon as
- As though
- Provided that
- Supposing
- Than
Correlative Conjunctions:
- ..and
- ..or
- ..nor
- Not only…but also
- ..or
Conjunctive Adverbs (used like conjunctions):
- However
- Moreover
- Therefore
- Consequently
- Furthermore
- Otherwise
- Instead
- Meanwhile
- Nonetheless
- Accordingly
- Besides
- Still
- Thus
- Hence
- Similarly
- Namely
Good job. Thank you. I had downloaded some of the pdfs. Tqvm again.
Good job. Thank you. I had downloaded some of the pdfs.
I shall appreciate a lot if this comments box made me easy, without troubling a lot.