Verbs are the core of a sentence, expressing actions, occurrences, or states of being, and are essential in conveying the time and manner of any event.
Verbs in English Grammar
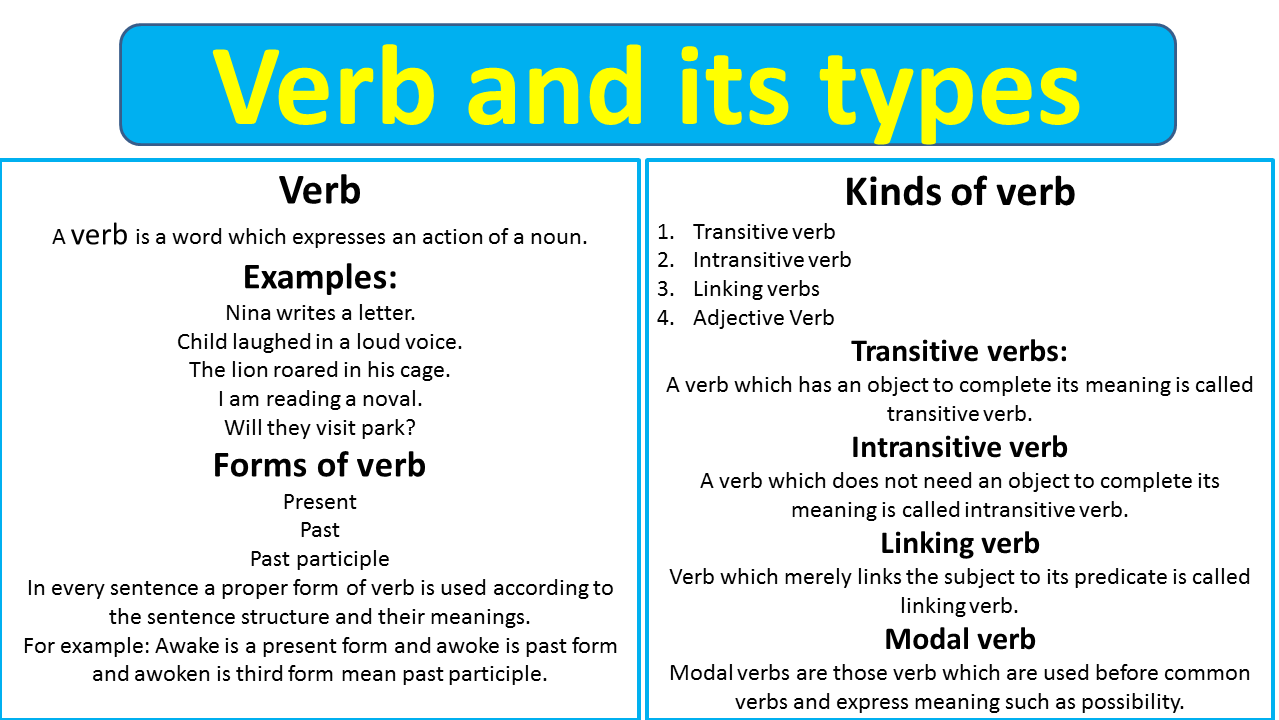
Verbs are the action words in a sentence that describe what is happening. They form the heart of the predicate in a sentence. In English grammar, verbs can show a variety of actions, states of being, or occurrences. They can indicate the time of an action (past, present, future) through their tense, the nature of the action (completed or ongoing) through aspect, and the voice (active or passive) of the action.
What are Verbs and their types?
Definition of Verb:
A verb is a part of speech that expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being. Verbs are essential components of a sentence as they indicate what the subject is doing or what is happening.
Types of Verbs with Examples
Action Verbs
Action verbs express specific actions, whether they are physical or mental.
- I can see the bird in the tree.
- She loves to read mystery novels.
- The cat purred
- He runs every morning.
- They spoke in hushed tones.
- You write beautiful poetry.
- She dances with elegance.
- We accepted the offer gratefully.
- He thinks deeply about these issues.
- The teacher always encourages her students.
- She lifted the box with ease.
- They traveled across Europe last summer.
- He sang a lovely melody.
- The dog barked
- You played the piano wonderfully.
- The baby cried throughout the night.
- She jumped with joy.
- The phone rang
- He whispered the secret to her.
- I noticed a mistake in the report.
Linking Verbs
Linking verbs connect the subject to additional information about the subject. They do not show action.
- She is a teacher.
- The cake smells
- He seems upset about the news.
- The soup tastes
- The flowers look
- The book appears to be old.
- She became a successful lawyer.
- The sky grew
- The baby feels
- The story sounds
- That seems
- The results were
- The fabric feels
- The night became
- The movie was
- The room smells like fresh paint.
- Her advice sounds
- The idea seems
- The task appears
- The milk tastes
Must Learn About:
Nouns, Pronouns, Verbs, Adjectives, Adverbs, Interjections, Prepositions, Conjunctions
Auxiliary (Helping) Verbs
Auxiliary verbs are used together with a main verb to show the verb’s tense or to form a question or negative.
- She can play the guitar.
- I have finished my homework.
- We will go to the park later.
- You must stop here.
- He should
- They might come to the party.
- She does not like spinach.
- I did not hear the alarm.
- We are leaving soon.
- He has been working all day.
- You were sleeping when I called.
- They have been studying for hours.
- She is writing a letter.
- He was walking his dog.
- You shall not pass.
- I would like to order dessert.
- They had left by the time we arrived.
- You could see the excitement on her face.
- He will have been waiting for an hour.
- I am going to the market.
Modal Verbs
Modal verbs are a type of auxiliary verb that express necessity, possibility, permission, or ability.
- You must finish your work.
- She can solve difficult puzzles.
- They might arrive late.
- He should improve his diet.
- We would like to start now.
- You shall pass the exam.
- She could see the finish line.
- They may come to the meeting.
- I will be able to see you tomorrow.
- He ought to apologize.
- You mustn’t smoke here.
- She couldn’t believe her eyes.
- They wouldn’t accept the offer.
- I shall write to you soon.
- You might want to check that.
- He can’t have taken it.
- We shouldn’t be late.
- You won’t regret this decision.
- She may have left already.
- They could not find the place.
Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs do not follow the standard rules of conjugation in the past tense and past participle forms.
- I spoke to him yesterday.
- She woke up late this morning.
- He wore his new shoes.
- We ate at a new restaurant.
- They drank all the lemonade.
- You gave me the wrong directions.
- She saw a rare bird.
- He went to the store.
- I took the wrong bus.
- You broke your promise.
- She has done her best.
- He drove his car carefully.
- We flew to Paris last summer.
- They swam across the lake.
- You were really helpful.
- I have seen that movie before.
- She had written three books by then.
- He was known for his wisdom.
- We bought a new house.
- They thought it was a good idea.
Transitive Verbs
Transitive verbs require a direct object to complete their meaning.
- She plays the violin gracefully.
- He reads the newspaper every morning.
- The teacher assigns homework daily.
- We admire the artist’s work.
- The chef tastes the dish before serving.
Intransitive Verbs
Intransitive verbs do not require a direct object to complete their meaning.
- The baby slept
- Birds migrate as seasons change.
- He smiled
- She jogged regularly at dawn.
- The sun sets in the west.
Phrasal Verbs
Phrasal verbs consist of a verb and a preposition or adverb that changes the meaning of the verb.
- He looked up the word in the dictionary.
- We ran into an old friend at the cafe.
- She turned off the lights before leaving.
- They brought up an interesting point during the meeting.
- I came across an old photo album in the attic.
Finite Verbs
Finite verbs are verbs that have a subject and are conjugated to show tense.
- She writes letters to her pen pal.
- The children play in the park.
- He is going to the store now.
- We were watching the stars last night.
- They have completed their assignments.
Non-finite Verbs
Non-finite verbs do not show tense, person, or number. They include infinitives, participles, and gerunds.
- To run in the marathon requires stamina. (Infinitive)
- Running marathons is her hobby. (Gerund)
- The barking dog kept us awake. (Present participle)
- Baked fresh, the bread smells wonderful. (Past participle)
- She had a suggestion to make. (Infinitive)
Examples of Verbs in sentences
- Birds chirp at dawn.
- Waves crash against the shore.
- Children laugh
- The wind whistles through trees.
- Rain patters on the roof.
- Stars twinkle in the night sky.
- Leaves rustle in the breeze.
- Students study for exams.
- Chefs cook delicious meals.
- Runners sprint to the finish line.
- Fish swim in the pond.
- The sun shines
- The clock ticks
- Trains arrive at the station.
- Actors perform on stage.
- Bakers knead dough for bread.
- A cat pounces on a toy.
- Mechanics fix broken engines.
- Athletes train for the Olympics.
- Teachers explain complex topics.
- Writers create new worlds.
- Flowers bloom in spring.
- Bees buzz around flowers.
- Snowflakes drift to the ground.
- The moon glows in the dark.
- Drummers beat their drums.
- The fire crackles
- A baby coos
- A horse trots along the path.
- A doorbell rings
- A photographer captures the moment.
- Trees shed their leaves in fall.
- A bell tolls in the distance.
- Artists paint stunning landscapes.
- Butterflies flutter
- A comedian jokes on stage.
- A singer croons a love song.
- A snake slithers in the grass.
- A judge decides on the verdict.
- A doctor diagnoses the ailment.
- A baby gurgles
- A teacher grades
- A dancer leaps in the air.
- A jeweler crafts a ring.
- A librarian organizes the books.
- A tailor sews a dress.
- A painter varnishes the wood.
- A pilot navigates the skies.
- A diver explores the ocean depths.
- A gardener prunes the bushes.
- A golfer swings the club.
- A thief steals a wallet.
- A writer scribbles
- A judge sits in court.
- A chef slices the vegetables.
- A teacher lectures in class.
- A driver honks the horn.
- A bird builds a nest.
- A child scribbles with crayons.
- A dog digs a hole.
- A farmer harvests the crops.
- A sailor sails the sea.
- A lion roars in the jungle.
- A student calculates the answer.
- A programmer codes a new app.
- A fisherman casts a line.
- A pilot flies a plane.
- A climber ascends the mountain.
- A speaker addresses the audience.
- A swimmer dives into the pool.
- A skier glides down the slope.
- A boxer punches the bag.
- A driver accelerates the car.
- A reader flips through pages.
- A baker glazes a donut.
- A carpenter sands the wood.
- A dog barks at strangers.
- A detective investigates a mystery.
- A fish gulps
- A guest arrives at the party.
- A boy whispers a secret.
- A director films a scene.
- A guest knocks on the door.
- A baby suckles
- A cat yawns
- A teacher points to the board.
- A student erases an error.
- A dog wags its tail.
- A guest greets the host.
- A child hugs a teddy bear.
- A baker rolls out dough.
- A painter dips the brush.
- A musician strums a guitar.
- A dog licks its owner.
- A child picks
- A bird soars in the sky.
- A customer pays the bill.
- A reader enjoys a good book.
- A cat scratches the post.
- A teacher inspires her students.
Verb and its Types with Examples PDF | Images