Parts of speech Definitions and examples play very important roles in English grammar. Parts of speech are fundamental building blocks in the structure of any language. Understanding them is essential for mastering grammar, enhancing writing skills, and improving overall communication. In English, parts of speech categorize words based on their function and the role they play in sentences.
This classification helps in identifying how words interact with each other to form meaningful sentences. There are eight primary parts of speech in English, each serving a unique purpose in sentence construction.
These include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. By comprehending these categories, students can better grasp the complexities of English grammar and improve their linguistic abilities.
Parts Of Speech Definitions And Examples
Parts of speech are categories of words that serve specific functions and play specific roles in the structure of sentences in the English language. Here are the main parts of speech with their definitions:
- Nouns: Words that name persons, places, things, or ideas. Examples include “dog,” “city,” and “happiness.”
- Pronouns: Words that take the place of nouns. Examples include “he,” “they,” and “which.”
- Verbs: Words that express actions or states of being. Examples include “run,” “is,” and “think.”
- Adjectives: Words that describe or modify nouns. Examples include “red,” “happy,” and “fast.”
- Adverbs: Words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, often indicating manner, time, place, or degree. Examples include “quickly,” “very,” and “there.”
- Prepositions: Words that show relationships between nouns (or pronouns) and other words in a sentence. Examples include “in,” “on,” and “by.”
- Conjunctions: Words that connect words, phrases, or clauses. Examples include “and,” “but,” and “or.”
- Interjections: Words that express emotion, often used as exclamations and are typically followed by a comma or an exclamation point. Examples include “Wow!,” “Ouch!,” and “Hey!”
Must Learn About:
Nouns, Pronouns, Verbs, Adjectives, Adverbs, Interjections, Prepositions, Conjunctions
List of All Parts of Speech
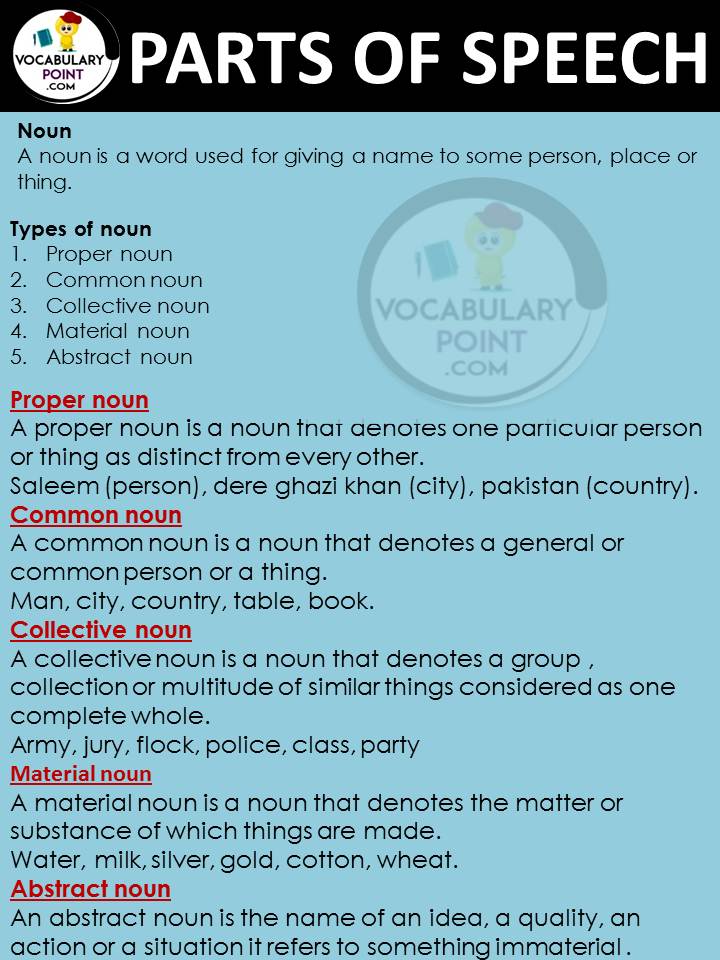
Noun
Definition
A noun is a word used to identify any of a class of people, places, things, or ideas. It can act as the subject or object of a verb, the object of a preposition, or can modify another noun.
Examples of Nouns
- Cat
- River
- Book
- Happiness
- Apple
- London
- Doctor
- Chair
- School
- Music
Examples of Nouns in Sentences
- The cat sat on the mat.
- The river flows gently towards the sea.
- She read an interesting book about history.
- His happiness was evident from his smile.
- She ate an apple for lunch.
- They traveled to London last summer.
- The doctor will see you now.
- She bought a new chair for her room.
- The children go to school every weekday.
- She loves listening to classical music.
Types of Noun
- Proper Nouns: Names of specific people, places, or organizations. They are always capitalized and identify unique entities.
- Common Nouns: General names for a person, place, thing, or idea. They are not capitalized unless they start a sentence.
- Concrete Nouns: Represent physical objects or substances that can be sensed through the five senses.
- Abstract Nouns: Names of ideas, qualities, or states that cannot be seen or touched.
- Countable Nouns: Nouns that can be counted, having both singular and plural forms.
- Uncountable Nouns: Substances, concepts, etc., that cannot be divided into separate elements and do not have a plural form.
- Collective Nouns: Refer to groups of people, animals, or things.
List of Nouns
- Ambulance: Emergency
- Butterfly: Insect
- Cupcake: Dessert
- Diamond: Gemstone
- Eclipse: Celestial
- Festival: Celebration
- Glacier: Ice
- Harmony: Unity
- Igloo: Shelter
- Jungle: Forest
- Kangaroo: Marsupial
- Lantern: Light
- Mountain: Terrain
- Nest: Home
- Orchestra: Music
- Pirate: Outlaw
- Quilt: Bedding
- Rainbow: Spectrum
- Sunflower: Plant
- Telescope: Instrument
- Unicorn: Mythical
- Volcano: Eruption
- Waterfall: Nature
- Xylophone: Instrument
- Yacht: Boat
- Zeppelin: Aircraft
- Anchor: Stability
- Balloon: Inflate
- Comet: Astronomical
- Dolphin: Mammal
- Empire: Dominion
- Feather: Plumage
- Guitar: Music
- Helmet: Protection
- Island: Landmass
- Jewel: Precious
- Kettle: Appliance
- Lighthouse: Beacon
- Magnet: Attraction
- Noodle: Food
- Oasis: Refuge
- Penguin: Bird
- Quartz: Mineral
- Robot: Machine
- Statue: Sculpture
- Tornado: Storm
- Umbrella: Rain
- Vaccine: Immunization
- Windmill: Energy
- Yarn: Thread
Pronouns
Definition
Pronouns are words that substitute for nouns or noun phrases, making sentences less repetitive and more efficient. They are used to avoid repeating the same nouns over and over again.
Examples
- He: Refers to a male person or animal.
- She: Refers to a female person or animal.
- It: Refers to a thing, animal, or a concept.
- They: Refers to people, animals, or things in the plural.
- You: Addresses the person or people being spoken or written to.
Examples in Sentence
- He is going to the store.
- She loves to read books.
- It is raining outside.
- They are coming over for dinner.
- You should try this cake.
Types of Pronouns
- Personal Pronouns: Refer to specific people or things.
- Example: I, you, he, she, it, we, they.
- Possessive Pronouns: Indicate ownership or possession.
- Example: mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs.
- Reflexive Pronouns: Refer back to the subject of the sentence.
- Example: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves.
- Demonstrative Pronouns: Point to specific things.
- Example: this, that, these, those.
- Relative Pronouns: Introduce relative clauses, connecting them to main clauses.
- Example: who, whom, whose, which, that.
- Interrogative Pronouns: Used to ask questions.
- Example: who, whom, whose, which, what.
- Indefinite Pronouns: Refer to nonspecific things or people.
- Example: anyone, everybody, nothing, each, few, many, someone.
List of Pronouns
- I
- Me
- We
- Us
- You
- He
- Him
- She
- Her
- It
- They
- Them
- My
- Mine
- Our
- Ours
- Your
- Yours
- His
- Hers
- Its
- Their
- Theirs
- Myself
- Ourselves
- Yourself
- Yourselves
- Himself
- Herself
- Itself
- Oneself
- Themselves
- This
- That
- These
- Those
- Who
- Whom
- Whose
- Which
- What
- Whoever
- Whomever
- Whichever
- Whatever
- All
- Another
- Any
- Anybody
- Anyone
Verbs
Definition
Verbs are words that describe an action, an occurrence, or a state of being. They are fundamental components of sentences, indicating what the subject is doing or the condition they are in.
Examples
- Run: To move quickly on foot.
- Eat: To consume food.
- Sing: To produce musical sounds with the voice.
- Jump: To spring off the ground.
- Write: To form letters or words on a surface.
- Laugh: To express amusement audibly.
- Sleep: To rest in a state of reduced consciousness.
- Think: To consider or reflect mentally.
- Play: To engage in a game or recreational activity.
- Read: To look at and comprehend the meaning of written or printed material.
Examples in Sentence
- Run: “The athlete can run very fast.”
- Eat: “We should eat more vegetables.”
- Sing: “She loves to sing in the choir.”
- Jump: “The children like to jump on the trampoline.”
- Write: “He can write a novel.”
- Laugh: “They often laugh at funny jokes.”
- Sleep: “The cat likes to sleep in the sun.”
- Think: “I need to think about this decision.”
- Play: “The kids play outside after school.”
- Read: “She enjoys reading mystery novels.”
Types of Verbs
- Action Verbs: Express physical or mental actions.
- Example: Run, Eat, Sing, Jump, Write.
- Linking Verbs: Connect the subject to more information about the subject.
- Example: Am, Is, Are, Was, Were.
- Auxiliary Verbs: Help the main verb and are used with a main verb to show the verb’s tense or to form a question or negative.
- Example: Have, Has, Had, Do, Does.
- Modal Verbs: Express necessity, possibility, permission, or ability.
- Example: Can, Could, May, Might, Must.
- Transitive Verbs: Require a direct object.
- Example: Throw, Bring, Buy, Send, Give.
- Intransitive Verbs: Do not require a direct object.
- Example: Go, Lie, Arrive, Die, Fall.
List of Verbs
- Ask: Inquire
- Believe: Accept as true
- Create: Produce
- Decide: Choose
- Enjoy: Delight in
- Follow: Pursue
- Help: Assist
- Listen: Hear attentively
- Remember: Recall
- Use: Employ
- Walk: Move on foot
- Learn: Acquire knowledge
- Teach: Instruct
- Grow: Increase
- Open: Uncover
- Close: Shut
- Start: Begin
- Finish: Complete
- Laugh: Express humor
- Cry: Shed tears
- Dance: Move rhythmically
- Sing: Vocalize melodies
- Jump: Leap
- Run: Race swiftly
- Drive: Operate a vehicle
- Fly: Soar through air
- Swim: Move in water
- Climb: Ascend
- Sit: Rest on a seat
- Stand: Be upright
- Speak: Talk
- Whisper: Speak softly
- Shout: Yell
- Write: Compose text
- Read: Perceive written words
- Calculate: Compute numbers
- Draw: Make art
- Paint: Apply color
- Build: Construct
- Design: Plan
- Invent: Create something new
- Discover: Find
- Explore: Investigate
- Travel: Journey
- Arrive: Reach a place
- Leave: Depart
- Enter: Come in
- Exit: Go out
- Throw: Propel through air
- Catch: Grab
- Push: Apply force
- Pull: Draw towards
- Lift: Raise
- Carry: Transport
- Move: Change position
- Stop: Cease movement
- Watch: Observe
- See: Perceive visually
- Hear: Perceive sound
- Taste: Sense flavor
- Touch: Make contact
- Smell: Detect odors
- Buy: Purchase
- Sell: Trade
- Pay: Give money
- Charge: Demand payment
- Save: Preserve
- Waste: Use carelessly
- Clean: Make neat
- Dirty: Make unclean
- Cook: Prepare food
- Eat: Consume food
- Drink: Consume liquid
- Bite: Use teeth
- Chew: Grind with teeth
- Kiss: Touch with lips
- Hug: Embrace
- Fight: Combat
- Play: Engage in fun
- Rest: Relax
- Work: Do a job
- Practice: Rehearse
- Perform: Execute a task
- Win: Achieve victory
- Lose: Fail to win
- Tie: Draw
- Compete: Take part in a contest
- Agree: Concur
- Disagree: Differ
- Argue: Debate
- Discuss: Talk about
- Explain: Make clear
- Describe: Portray
- Predict: Foretell
- Forget: Fail to remember
- Recall: Remember
- Imagine: Visualize
- Dream: Experience while sleeping
- Hope: Desire with expectation
- Wish: Desire
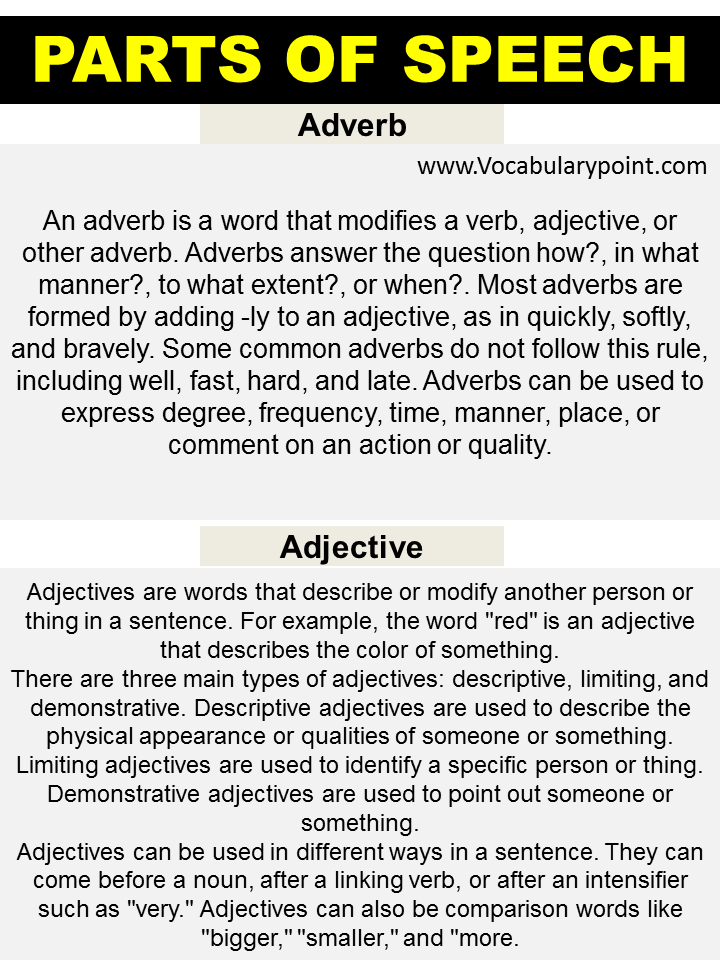
Adverbs
Definition
Adverbs are words that modify a verb, an adjective, another adverb, or even a whole sentence. They provide additional information about how, when, where, to what extent, or under what condition something happens.
Examples
- Quickly: With speed.
- Silently: Without sound.
- Happily: With happiness.
- Often: Frequently.
- Very: To a high degree.
- Really: Truly or genuinely.
- Easily: Without difficulty.
- Yesterday: On the day before today.
- Outside: In an external place.
- Here: In this place.
Examples in Sentence
- Quickly: “She runs quickly.”
- Silently: “He walked silently into the room.”
- Happily: “They lived happily ever after.”
- Often: “I often go for a walk in the park.”
- Very: “This is a very important issue.”
- Really: “I really enjoy this book.”
- Easily: “He solved the puzzle easily.”
- Yesterday: “I met him yesterday.”
- Outside: “The dog is playing outside.”
- Here: “We are here at the concert.”
Types of Adverbs
- Adverbs of Manner: Describe how something happens.
- Example: Quickly, Slowly, Easily, Happily, Silently.
- Adverbs of Time: Indicate when something happens.
- Example: Now, Later, Soon, Yesterday, Today.
- Adverbs of Place: Show where something happens.
- Example: Here, There, Everywhere, Inside, Outside.
- Adverbs of Frequency: Describe how often something happens.
- Example: Always, Often, Seldom, Never, Usually.
- Adverbs of Degree: Indicate the level or extent of something.
- Example: Very, Quite, Almost, Too, Enough.
List of Adverb
- Abruptly: Suddenly
- Absolutely: Completely
- Accidentally: Unintentionally
- Actually: In fact
- Almost: Nearly
- Altogether: Completely
- Always: At all times
- Angrily: With anger
- Anxiously: With anxiety
- Anywhere: In any place
- Apparently: Seemingly
- Approximately: Roughly
- Badly: Poorly
- Barely: Hardly
- Beautifully: In a beautiful manner
- Before: Earlier
- Blindly: Without seeing
- Boldly: With courage
- Bravely: Courageously
- Briefly: For a short time
- Brightly: With brightness
- Briskly: Quickly
- Calmly: In a calm manner
- Carefully: With care
- Carelessly: Without care
- Certainly: Surely
- Cheerfully: With cheer
- Clearly: With clarity
- Closely: Near
- Commonly: Usually
- Constantly: Continuously
- Correctly: Rightly
- Courageously: With courage
- Daily: Every day
- Deliberately: Intentionally
- Delightfully: Pleasingly
- Doubtfully: With doubt
- Eagerly: With eagerness
- Early: Before the expected time
- Easily: Without difficulty
- Effectively: In an effective manner
- Efficiently: Competently
- Elegantly: With elegance
- Equally: In equal parts
- Especially: Particularly
- Essentially: Fundamentally
- Eternally: Forever
- Evenly: Uniformly
- Eventually: In the end
- Exactly: Precisely
- Exceedingly: Extremely
- Exceptionally: Unusually
- Excitedly: With excitement
- Exclusively: Solely
- Extremely: To a great extent
- Fairly: Justly
- Faithfully: Loyally
- Famously: Well-known
- Far: At a great distance
- Fast: Quickly
- Fatally: Lethally
- Fiercely: Violently
- Firmly: Solidly
- Firstly: In the first place
- Flatly: Without emotion
- Fondly: With affection
- Foolishly: Without sense
- Formally: Officially
- Frequently: Often
- Fully: Completely
- Generally: Usually
- Generously: Liberally
- Gently: Softly
- Gladly: With pleasure
- Gracefully: With grace
- Gratefully: With gratitude
- Greatly: Immensely
- Grimly: Sternly
- Happily: Joyfully
- Hard: With effort
- Harshly: Severely
- Hastily: Quickly
- Heartily: Enthusiastically
- Heavily: With weight
- Helpfully: In a helpful manner
- Honestly: Truthfully
- Hopelessly: Without hope
- Hourly: Every hour
- Humbly: Modestly
- Immediately: Instantly
- Immensely: Vastly
- Impatiently: Without patience
- Impolitely: Rudely
- Important: Significantly
- Incorrectly: Wrongly
- Indefinitely: For an undefined period
- Independently: On one’s own
- Indoors: Inside a building
- Inevitably: Unavoidably
- Infinitely: Endlessly



Adjectives
Definition
Adjectives are words that describe or modify another person or thing in the sentence, typically a noun. They can provide information about the size, shape, age, color, origin, material, or purpose of a noun.
Examples
- Beautiful: Pleasing to the senses.
- Large: Of considerable size.
- Happy: Feeling or showing pleasure.
- Ancient: Very old.
- Cold: Low in temperature.
- Bright: Giving out or reflecting much light.
- Soft: Easy to mold, cut, compress, or fold.
- Red: Having the color of blood or cherries.
- Fast: Moving at high speed.
- Young: Having lived or existed for only a short time.
Examples in Sentence
- Beautiful: “The garden is beautiful in spring.”
- Large: “They have a large“
- Happy: “She felt happy after receiving good news.”
- Ancient: “They visited the ancient“
- Cold: “The water was too cold for swimming.”
- Bright: “The room was bright with sunlight.”
- Soft: “The kitten’s fur is very soft.”
- Red: “She wore a red“
- Fast: “The car is incredibly fast.”
- Young: “Their young son is starting school.”
Types of Adjectives
- Descriptive Adjectives: Describe the qualities or states of being of nouns.
- Example: Happy, Sad, Bright, Dark, Loud.
- Quantitative Adjectives: Indicate the quantity of a noun.
- Example: Many, Few, Several, Whole, No.
- Demonstrative Adjectives: Point out specific nouns.
- Example: This, That, These, Those.
- Possessive Adjectives: Show ownership or possession.
- Example: My, Your, His, Her, Their.
- Interrogative Adjectives: Used in questions.
- Example: Which, What, Whose.
- Comparative Adjectives: Compare two things.
- Example: Bigger, Smaller, Faster, Higher, Lower.
- Superlative Adjectives: Express the extreme or highest degree.
- Example: Biggest, Smallest, Fastest, Highest, Lowest.
- Articles: Define a noun as specific or unspecific.
- Example: A, An, The.
List of Adjective
- Adorable: Endearing
- Adventurous: Daring
- Aggressive: Forceful
- Alert: Watchful
- Attractive: Appealing
- Average: Ordinary
- Awful: Terrible
- Bad: Poor quality
- Beautiful: Pleasing
- Blue: Color
- Bold: Confident
- Brave: Courageous
- Bright: Shiny
- Brilliant: Very smart
- Calm: Peaceful
- Careful: Cautious
- Charming: Delightful
- Cheerful: Happy
- Clean: Not dirty
- Clear: Understandable
- Clever: Intelligent
- Close: Near
- Cold: Chilly
- Colorful: Full of color
- Comfortable: Cozy
- Concerned: Worried
- Confident: Self-assured
- Confused: Puzzled
- Cool: Slightly cold
- Cooperative: Helpful
- Courageous: Brave
- Crazy: Insane
- Creative: Inventive
- Cruel: Mean
- Curious: Inquisitive
- Cute: Adorable
- Dangerous: Unsafe
- Dark: Not light
- Dead: Not alive
- Decent: Proper
- Delicate: Fragile
- Delightful: Pleasing
- Depressed: Sad
- Determined: Resolute
- Different: Not the same
- Difficult: Not easy
- Dirty: Not clean
- Disgusted: Revolted
- Distinct: Clear
- Disturbed: Upset
- Dizzy: Unsteady
- Dull: Boring
- Eager: Keen
- Easy: Simple
- Educated: Learned
- Efficient: Effective
- Elegant: Graceful
- Embarrassed: Ashamed
- Empty: Nothing inside
- Enchanted: Charmed
- Encouraging: Inspiring
- Energetic: Active
- Enormous: Very big
- Enthusiastic: Excited
- Evil: Very bad
- Excited: Thrilled
- Expensive: High-priced
- Fair: Just
- Faithful: Loyal
- Famous: Well-known
- Fancy: Elaborate
- Fantastic: Great
- Fierce: Intense
- Filthy: Very dirty
- Fine: Good
- Foolish: Unwise
- Fragile: Breakable
- Friendly: Kind
- Frightened: Scared
- Funny: Humorous
- Generous: Giving
- Gentle: Mild
- Giant: Very large
- Glamorous: Fascinating
- Gleaming: Shining
- Glorious: Wonderful
- Good: Positive
- Gorgeous: Very beautiful
- Graceful: Elegant
- Grateful: Thankful
- Great: Excellent
- Greedy: Wanting more
- Green: Color
- Grim: Serious
- Grouchy: Grumpy
- Grumpy: Bad-tempered
- Handsome: Good-looking
- Happy: Joyful
- Hard: Solid
- Harsh: Severe
Prepositions
Definition
Prepositions are words used to link nouns, pronouns, or phrases to other words within a sentence. They act to connect the people, objects, time, and locations of a sentence.
Examples
- In: Inside or within.
- On: Positioned at the top of.
- At: A point or location.
- From: The point of origin.
- With: Accompanied by.
- By: Means of.
- Over: Above or higher than.
- Under: Beneath or lower than.
- Between: In the middle of two points.
- Against: In opposition to.
Examples in Sentence
- In: “The cat is in the box.”
- On: “The book is on the table.”
- At: “Meet me at the mall.”
- From: “She traveled here from New York.”
- With: “He came with his friends.”
- By: “The letter was written by“
- Over: “The plane flew over the mountains.”
- Under: “The dog hid under the bed.”
- Between: “The park is between the museum and the library.”
- Against: “He leaned against the wall.”
Types of Prepositions
- Time Prepositions: Refer to time.
- Example: Before, After, During, Until, Since.
- Place Prepositions: Indicate location or position.
- Example: Above, Below, Inside, Outside, Around.
- Direction Prepositions: Show direction.
- Example: To, From, Up, Down, Towards.
- Prepositions of Agents or Things: Indicate a causal relationship.
- Example: By, With, Of, For, Against.
- Prepositions of Manner: Show the manner or way something happens.
- Example: By, On, In, Like, As.
List of Preposition Words
- About: Concerning
- Above: Overhead
- Across: From one side to another
- After: Following in time
- Against: Opposed to
- Along: By the length of
- Among: In the middle of
- Around: Surrounding
- As: Similar to
- At: In a specific place
- Before: Prior to
- Behind: At the back of
- Below: Beneath
- Beneath: Underneath
- Beside: Next to
- Between: In the middle of two
- Beyond: Past the limit of
- But: Except for
- By: Close to or beside
- Concerning: Regarding
- Considering: Taking into account
- Despite: Without being affected by
- Down: From a higher to a lower point
- During: Throughout the duration of
- Except: Not including
- For: Intended to belong to
- From: Starting point
- In: Inside
- Inside: Within
- Into: Entering
- Like: Similar to
- Near: Close by
- Next: Following
- Of: Belonging to
- Off: Away from
- On: Resting at the surface
- Onto: Moving to the top of
- Out: Exiting
- Outside: Not inside
- Over: Above
- Past: Beyond
- Regarding: Concerning
- Round: Circular motion
- Since: From a time in the past
- Through: From end to end
- Throughout: All the way through
- Till: Up to the time of
- To: In the direction of
- Towards: In the direction of
- Under: Beneath
- Underneath: Directly below
- Unlike: Different from
- Until: Up to the time of
- Up: Towards a higher place
- Upon: On top of
- Versus: Against
- Via: By way of
- With: Accompanied by
- Within: Inside
- Without: Lacking
- According to: As stated by
- Adjacent to: Next to
- Ahead of: In front of
- Alongside: Next to
- Amid: Among
- Amongst: In the middle of
- Apart from: Excluding
- As for: Regarding
- Aside from: Apart from
- Because of: Due to
- Close to: Near
- Due to: Caused by
- Except for: Other than
- Far from: Not near
- In addition to: Also
- In between: Among
- In front of: Before
- In place of: Instead of
- In spite of: Despite
- Instead of: In place of
- On account of: Because of
- On behalf of: Representing
- On top of: Above
- Opposite: Facing
- Out of: From within to the outside
- Outside of: Beyond
- Owing to: Because of
- Prior to: Before
- Regardless of: No matter
- Subsequent to: After
- Such as: For example
- Thanks to: Because of
- Together with: Along with
- Up against: Facing or opposing
- Up to: As far as
- As opposed to: In contrast to
- As per: According to
- As well as: In addition to
- In accordance with: Following
Conjunctions
Definition
Conjunctions are words that join together other words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence. They help to create complex sentences, build connections, and add coherence to writing.
Examples
- And: Used to connect similar ideas.
- But: Indicates a contrast.
- Or: Presents an alternative or choice.
- Because: Shows a reason or cause.
- Although: Suggests a contrast in spite of something.
- Since: Indicates time or reason.
- Unless: Means ‘if not’.
- While: Indicates two things happening at the same time.
- Whereas: Shows a contrast between two things.
- After: Refers to time following an event.
Examples in Sentence
- And: “She bought apples and“
- But: “He wanted to go but he was too tired.”
- Or: “Would you like tea or coffee?”
- Because: “She smiled because she was happy.”
- Although: “Although it was raining, they went for a walk.”
- Since: “I have known her since“
- Unless: “We will not succeed unless we try.”
- While: “She listens to music while she studies.”
- Whereas: “I like tea, whereas he prefers coffee.”
- After: “After** the movie, we went to dinner.”
Types of Conjunctions
- Coordinating Conjunctions: Connect words, phrases, or clauses of equal importance.
- Example: And, But, Or, Nor, For, Yet, So.
- Subordinating Conjunctions: Connect an independent clause with a dependent clause.
- Example: Because, Although, Since, Unless, While.
- Correlative Conjunctions: Work in pairs to join words or phrases that are used in the same way in a sentence.
- Example: ..or, Neither…nor, Not only…but also, Both…and, Whether…or.
- Conjunctive Adverbs: Used to connect independent clauses and indicate the relationship between them.
- Example: However, Moreover, Therefore, Consequently, Nevertheless.
List of Conjunction
- And: Also
- But: However
- Or: Alternatively
- Because: Reason
- Although: Despite
- Since: From the time
- Unless: Except if
- While: During the time
- Whereas: In contrast
- After: Following
- Before: Prior to
- As: While
- If: On the condition
- Though: Even though
- When: At the time
- Whenever: At any time
- Till: Until
- Until: Up to the time
- Once: As soon as
- As soon as: Immediately when
- For: Because of
- Yet: Still
- So: Therefore
- ..or: Choice between two
- ..nor: Not either
- Not only…but also: Both
- ..and: Together
- ..or: Expressing a doubt
- Than: In comparison
- As if: Similarly
- As though: As if
- Even if: Regardless of whether
- Even though: Despite the fact
- Inasmuch as: Because
- Lest: For fear that
- Now that: Since
- Provided that: On the condition
- Seeing that: Considering
- Supposing that: Assuming
- While: Whereas
- Where: In which place
- Wherever: In any place
- How: In what way
- However: Nevertheless
- Moreover: Besides
- Therefore: As a result
- Consequently: As a result
- Nevertheless: Nonetheless
- Accordingly: Consequently
- Indeed: In fact
- Instead: As an alternative
- Otherwise: In a different way
- Plus: Additionally
- Thereby: As a result of
- Therefor: For that reason
- Though: However
- Thus: As a result
- Yet: Nonetheless
- Namely: Specifically
- As well as: And also
- Hence: Therefore
- Then: After that
- Ergo: Therefore
- Still: Nonetheless
- Albeit: Although
- Notwithstanding: In spite of
- In order to: For the purpose of
- So that: For the purpose
- As long as: Provided that
- As much as: To the extent that
- As soon as: Just after
- As far as: To the degree
- In that: Because
- Now when: At the time
- Insofar as: To the extent
- In the event that: If it happens
- Granted that: Assuming that
- In case: If it happens
- Whenever: At whatever time
- Wherein: In which
- Just as: Exactly like
- As: Similar to
- As if: As it would be if
- As though: As it would be if
- As far as: To the degree that
- As well as: In addition to
- As much as: To the extent of
- As soon as: Immediately when
- As long as: During the time that
- As soon as: Immediately when
- As much as: To the extent that
- As well as: In addition to
- As far as: To the extent of
- As soon as: Immediately when
- As long as: During the time that
- So as to: In order to
- So that: In order to
- In order that: For the purpose of
- So as to: For the purpose of
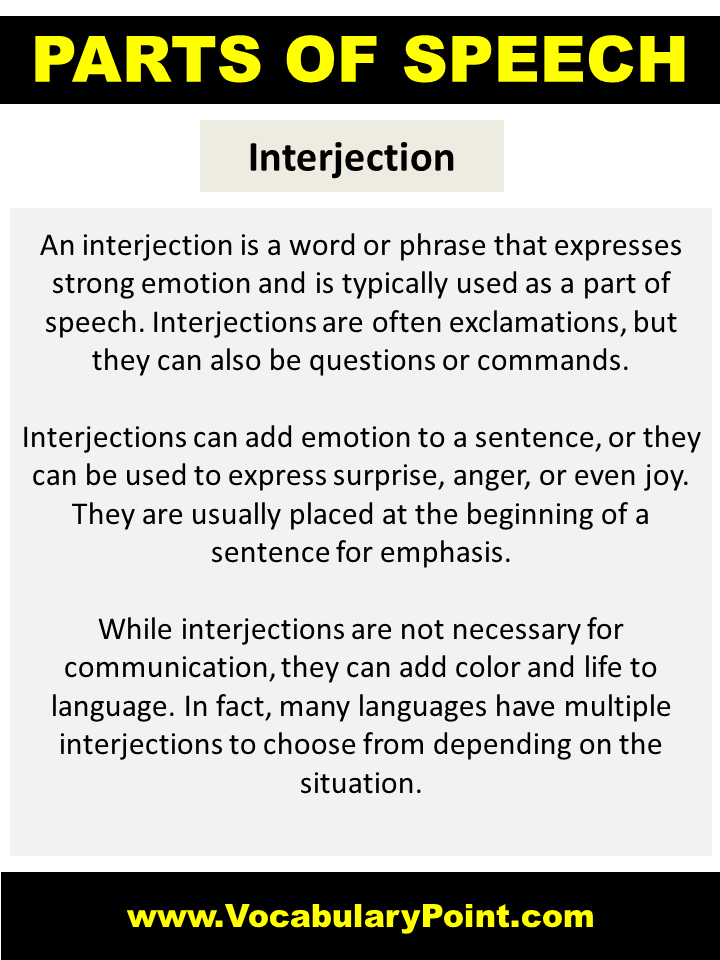
Interjection
Definition:
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses a strong emotion or reaction, often used spontaneously in speech. It typically stands alone and is often punctuated with an exclamation mark.
Examples:
- Ah
- Wow
- Oops
- Yay
- Alas
- Eek
- Aha
- Ouch
- Hooray
- Ugh
Examples in Sentences:
- Ah, now I understand!
- Wow, that’s amazing!
- Oops, I dropped it.
- Yay, we won the game!
- Alas, it was not meant to be.
- Eek, a spider!
- Aha, I’ve found the clue!
- Ouch, that hurt!
- Hooray, vacation starts today!
- Ugh, I can’t believe this happened.
Types of Interjection
- Joy
- g., Yay, Hooray, Woo-hoo, Yippee, Woohoo
- Yay, I got the job!
- Hooray, we won the match!
- Woo-hoo, this is so much fun!
- Yippee, it’s my birthday!
- Woohoo, we’re going on a trip!
- Surprise
- g., Wow, Oh, Whoa, Holy cow, Gee
- Wow, I didn’t see that coming!
- Oh, you scared me!
- Whoa, that was close!
- Holy cow, that’s a huge dog!
- Gee, that’s a brilliant idea!
- Pain
- g., Ouch, Ow, Eek, Yowch, Oof
- Ouch, I stubbed my toe!
- Ow, I burnt my hand!
- Eek, I cut myself!
- Yowch, that’s hot!
- Oof, I fell down the stairs.
- Disgust
- g., Ugh, Ew, Yuck, Gross, Ick
- Ugh, I hate broccoli.
- Ew, that smells bad.
- Yuck, this tastes awful.
- Gross, look at that mess.
- Ick, I stepped in mud.
- Relief
- g., Phew, Ahh, Ohh, Aah, Thank goodness
- Phew, that was a close call.
- Ahh, that feels better.
- Ohh, I finally finished my work.
- Aah, this is relaxing.
- Thank goodness, you are safe.
List of Interjection
- Ah: Realization or understanding
- Aha: Discovery or realization
- Alas: Sorrow or regret
- Bingo: Success or achievement
- Boo: Disapproval or surprise
- Bravo: Congratulations or approval
- Eek: Fear or alarm
- Eh: Inquiry or indifference
- Er: Hesitation
- Gee: Surprise or admiration
- Gosh: Surprise or amazement
- Ha: Laughter or triumph
- Haha: Laughter
- Heh: Amused laughter
- Hey: Attention or greeting
- Hi: Greeting
- Hm: Thought or consideration
- Hmm: Thinking or pondering
- Hooray: Joy or triumph
- Huh: Confusion or surprise
- Hum: Hesitation or thought
- Ick: Disgust
- Meh: Indifference or unimpressed
- Mhm: Agreement or acknowledgment
- Nah: Disagreement or refusal
- Nope: Negative response
- Oh: Surprise or realization
- Oho: Discovery or triumph
- Ooh: Amazement or pleasure
- Oops: Mistake or error
- Ouch: Pain
- Ow: Pain
- Phew: Relief
- Psst: Attention
- Shh: Quiet or silence
- Sigh: Disappointment or relief
- Tsk: Disapproval
- Uh: Hesitation
- Ugh: Disgust
- Uh-huh: Agreement
- Uh-oh: Concern or realization of a problem
- Um: Hesitation
- Whoa: Surprise or amazement
- Wow: Surprise or admiration
- Yay: Joy or excitement
- Yeah: Agreement or excitement
- Yikes: Fear or surprise
- Yippee: Joy or excitement
- Yo: Greeting or attention
- Yuck: Disgust
- Yup: Agreement
Parts of Speech with Examples and Definition | Image